To fully understand Bitcoin, one must fully understand private keys. In Bitcoin, the private key is what allows you to spend your coins and is the heart of how the system actually works. It is the reason that coins cannot be double spent and that value can be decentralized through a public blockchain not at risk of counterfeit or seizure.
<center></center>
<h1>What is a private key</h1>
A private key is simply a number, a number large enough to have an unthinkably massive sample space, a number with essentially infinite combinations.
Private keys are created by applying a mathematical algorithm to a truly random number. Say for example a private key is generated from the phrase “moonwalk”. The not-so-random phrase is generated into a private key. This is not a secure private key because anyone can try to guess at it since it’s a completely ordinary and common phrase. Someone right now is generating private keys from common phrases and emptying the wallets secured by these in-secure private keys.
<h1>Making sure its random</h1>
The heart of generating a secure private key is by starting with a truly random number. Good thing algorithms exist which can produce a truly random number. Now that the starting point is random, we can generate ourselves a fresh and secure private key. Again, the random number is such a large number in size means that it’s essentially impossible for another identical private key to be generated.
<center></center>
<h1>Here come the public keys</h1>
Once a proper private key is generated, elliptic curve cryptography is used to produce one or more public keys from the single private key. This process is a one-way trap door in that the private key can produce many public keys but any single public key cannot ever produce the parent private key.
Keep in mind that you do not need to be connected to the internet or interface with the blockchain or Bitcoin network to generate a private key. Since the rules of the game (mathematics) are universal, anyone can generate a truly random and secure private key, even without a computer.
A private key can be securely generated from a laptop booted from a CD instance of Ubuntu with the hard drive removed and never connected to the internet. Once the private key is generated, the laptop is shut down and nothing is stored. A Trezor or other hardware wallet can generate very secure private keys.
The private and public keys are mathematically linked. Nothing can cheat that link, resulting in an incredibly secure and resilient mechanism for storing scare digital value.
<h1>How the blockchain fits in</h1>
Now let’s get into how the block chain fits into this. Essentially the blockchain is a series of single blocks which contain many unique transactions within. Through a process of competition, the Bitcoin miners increase the blockchain height by securing new block to the previous ones. This happens about every 10 minutes.
<center>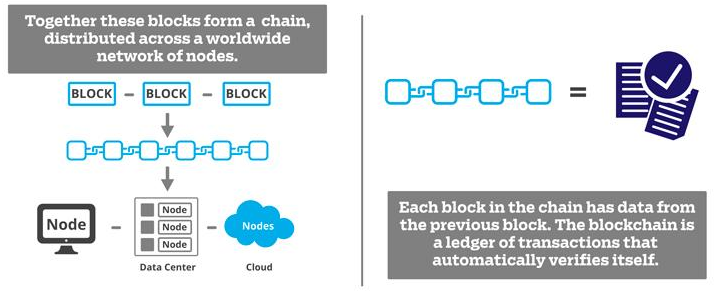</center>
<h1>Transactions</h1>
A transaction is simply an entry that shows coins moving from one public key to another. The sender of coins will broadcast to the network that some amount of coins needs to transfer to another public address. To prove ownership of the coins stored within a given public key in the blockchain, the sender must sign the transaction with the same private key used to hold the coins. This process happens in a secure environment and the private key is never exposed to the Bitcoin network or internet in general.
Since the private and public keys are related through mathematical forgery, the broadcasted transaction cannot be tampered with as it would be invalidated. Any alteration to the transaction invalidates the signature. The signature can only be reproduced with the linked private key.
Now that you see how private keys and public keys relate in a very specific uni-directional and mathematical manner, it makes it easier to see how value is secured and transferred in the blockchain.
<h1>Where are the Bitcoins?</h1>
The crazy thing about Bitcoin is that there aren’t any Bitcoins! There is only a series of transactions that show Bitcoin balances being added or subtracted to and from public keys. There are no Bitcoin in your paper wallet, hardware wallet or any other wallet. The term wallet in Bitcoin is misleading as there are no Bitcoin in your wallet but only a private key(s).
<h1>Wallet thoughts</h1>
When you are using a Trezor, your private key actually exists on the physical hardware itself. It’s stored electronically inside the device and nowhere else. When it broadcasts a transaction, it generates the signature using the private key. The private key never leaves the Trezor. The Trezor is able to secure your private key from malware and viruses via special hardware.

No matter what wallet you use, the private keys are never intentionally shared with the internet. However, private keys can easily be hacked if using a software wallet on the computer or web exchange that is not properly secured. When you stored Bitcoin on a wallet where you don’t control the private keys, like an exchange, then you are forced to trust them to secure your private key for you.
In the case of a paper wallet, the private key exists on that paper. If the paper is destroyed then the access to any Bitcoin under that private key is lost forever. The private key has an accompanying public key generated with it. If a transaction is sent to that public key, it exists as a transaction in the blockchian. Since your paper wallet's private key is mathematically forged to that public key and transaction, then the coins belong to it.

Make sure you read this a few times and go surf around Google for more information. The better you understand how private keys work in Bitcoin then the more powerful user you are.
<center>Have thoughts on the matter? Please say something below!</center>
<center>If you like the content you see, please follow for more like it.</center>
<hr>
<center><h1>🚀🚀🚀 Thanks for Reading 🚀🚀🚀</h1></center>
<table style="width:100%">
<tr>
<td><center><h1>
<p>Follow, Resteem and VOTE UP</p>
<p>@BitInformant</p>
<p><a href="https://twitter.com/Bit_Informant">Twitter</a></p>
<p><a href="https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCPFZTPGXT2Zlz-EIVHOaIqw">YouTube</a></p>
<p>Crypto & Tech Lovers</p></h1>
</center>
</td>
<td><img src="https://steemitimages.com/DQmQ4TyqUeVLvbjCYpcdW8RVf5y2jkaMCTJRh8EpzoDnaCC/image.png" width="30px"></td>
</tr>
</table> hiveblocks
hiveblocks