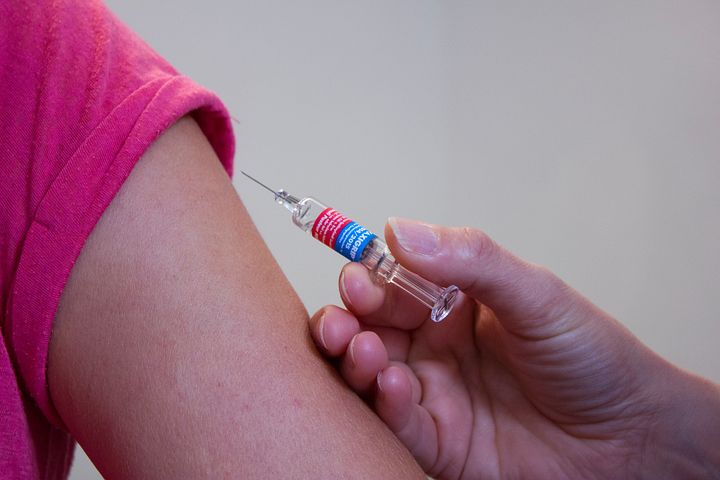
#### The process of administering a vaccine to aid the immune system in developing immunity to a disease is known as "vaccination".
[pixabay](https://pixabay.com/photos/vaccination-doctor-injection-1215279/)
Vaccination is an easy, safe, and effective way to protect yourself from potentially fatal diseases before coming into contact with them. It boosts your immune system by harnessing your body's natural defenses to help you fight off specific infections. Vaccines teach your immune system to produce antibodies in the same way it does when you are exposed to a disease. Vaccines, on the other hand, do not cause the disease or increase your chances of complications because they contain a weakened, live, or killed microorganism or virus, as well as proteins or toxins from the organism. They aid in the prevention of infectious disease illness by stimulating the body's immune system.
When a sufficiently large proportion of a population is immunized, herd immunity occurs. Herd immunity protects those who are immunocompromised and cannot receive a vaccine because even a weakened version would be toxic to them.
The effectiveness of vaccination has been extensively researched and validated. Vaccination is the most effective method of disease prevention; Vaccination-induced widespread immunity is largely responsible for the eradication of smallpox and the eradication of diseases such as polio and tetanus from much of the world. However, some diseases, such as measles outbreaks in the United States, have seen an increase in cases due to low vaccination rates in the 2010s, which can be attributed in part to vaccine hesitancy. Vaccination, according to the World Health Organization (WHO), saves 3.5-5 million lives each year.
[pixabay]([pixabay](https://pixabay.com/photos/woman-jetty-lake-rest-leisure-1784755/))
Although some diseases have become rare, the germs that cause them are still present in some or all parts of the world. In today's world, infectious diseases cross borders easily and infect anyone who is not protected. The two most important reasons to get vaccinated are to protect ourselves and those around us.
Germs can spread quickly through a community and sicken a large number of people. An outbreak may occur if a large number of people become ill. When a large number of people are immunized against a particular disease, germs cannot spread as easily from person to person — and the entire community is less likely to contract the disease. This means that even people who are unable to get vaccinated will be protected from getting sick.
> If a person does become ill, there is less of a chance of an outbreak because the disease is more difficult to spread.
Eventually, the disease becomes rare, and in some cases, it is eradicated entirely. Because not everyone can be vaccinated, such as very young babies, those who are seriously ill, or those who have certain allergies, they rely on others being vaccinated to ensure they are also protected from vaccine-preventable diseases.
**Conclusion**
Almost everyone can be vaccinated. However, due to certain medical conditions, some people should avoid or postpone receiving certain vaccines. Among these conditions are:
Chronic illnesses or treatments (such as chemotherapy) that have an impact on the immune system;
Severe and potentially fatal allergies to vaccine ingredients, which are extremely rare;
If you are sick and have a high fever on the day of your vaccination.
[pixabay](https://pixabay.com/link/?ua=cd3%3Dimage%26cd7%3Den%253Avaccination%253ANGA%26ec%3Dapi_ad%26ea%3Dnavigate%26el%3Dgetty%26tid%3DUA-20223345-1%26dr%3Dhttps%253A%252F%252Fpixabay.com%252Fimages%252Fsearch%252Fvacation%252F%253Fmanual_search%253D1&next=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.istockphoto.com%2Fphoto%2Felderly-lady-getting-immunization-via-anti-viral-vaccine-gm1340445660-420518768%3Futm_source%3Dpixabay%26utm_medium%3Daffiliate%26utm_campaign%3DSRP_image_sponsored%26utm_content%3Dhttps%253A%252F%252Fpixabay.com%252Fimages%252Fsearch%252Fvaccination%252F%253Fmanual_search%253D1%26utm_term%3Dvaccination&hash=f014447b22a29315aba625c6df4a3a70eb9fd451&=)
These factors frequently differ between vaccines. Consult your health care provider if you are unsure whether you or your child should receive a specific vaccine. They can assist you in making an informed decision about vaccination for yourself or your child. Everyone should be vaccinated but not everyone can be vaccinated. Those with some chronic illness and other factors should ensure they see their health consultant before undergoing a vaccination.
##### Thanks for reading
 hiveblocks
hiveblocks