<center></center>
With the many ways to secure a network, and devices, as well as data being transmitted, two of the most important methods of protection are Firewalls, and Interruption Detection Systems.
These two forms of security are well-known and tested, but they also offer different types and values when it comes to web security. In this short paper, we’ll discuss the similarities and differences, as well as best uses of each technology.
<center></center>
Firewalls provide a secure connection between the network devices, as well as secure communications between devices in a network. Firewalls can be used in a variety of situations, in both large-scale networks, and small, single-user home networks. A Firewall provides a separation between the user’s devices and files, and the outside web.
The Firewall is a defensive technology, used to block harmful transmissions from entering a network, or possibly from moving inside of a network.
With different sized networks, and therefore requirements, there are different types of Firewalls. These include, Proxy Firewalls, Packet Filtering Firewalls, Application-based Firewalls, and Stateful-Inspection Firewalls.
<center>!</center>
Packet Filtering Firewalls are the simplest Firewalls, which restrict traffic based on addresses. Stateful-Inspection Firewalls are slightly more complex to implement, and they can restrict packets based on addresses or the data contained in the header of the packet. Proxy Firewalls are even more comprehensive, as they allow for a full reading of the packet data, and decide to transmit based on results. The Proxy Server Firewall is configured to allow specific traffic to pass through the network. And lastly, Hybrid Firewalls are similar in this sense, and are both more intensive to implement in a network. (Kb.iu.edu/d/aoru 2013)
However, Firewalls are not perfect systems to deter unwanted traffic on a given network. For example, the Firewall is largely unable to effect internal traffic that has already bypassed the Firewall. The Firewall can also bottleneck, or strain under severe levels of traffic.
An Intrusion Detection System (IDS) is a set of technologies used to monitor suspicious actions and data transmitted to and from the network. Intrusion Detection Systems are described in two formats: Signature-Based and Anomaly Detection Systems.
Just like trusted users, attackers also have a signature that is recognizable by the network and some of the technologies being used. The IDS Signature-Based System evaluates these signatures for any inconsistencies or threats. These anomalies are logged by the IDS, and are evaluated on case by case basis. (Robert W., Timothy W., and Michael C. 2006)
<center>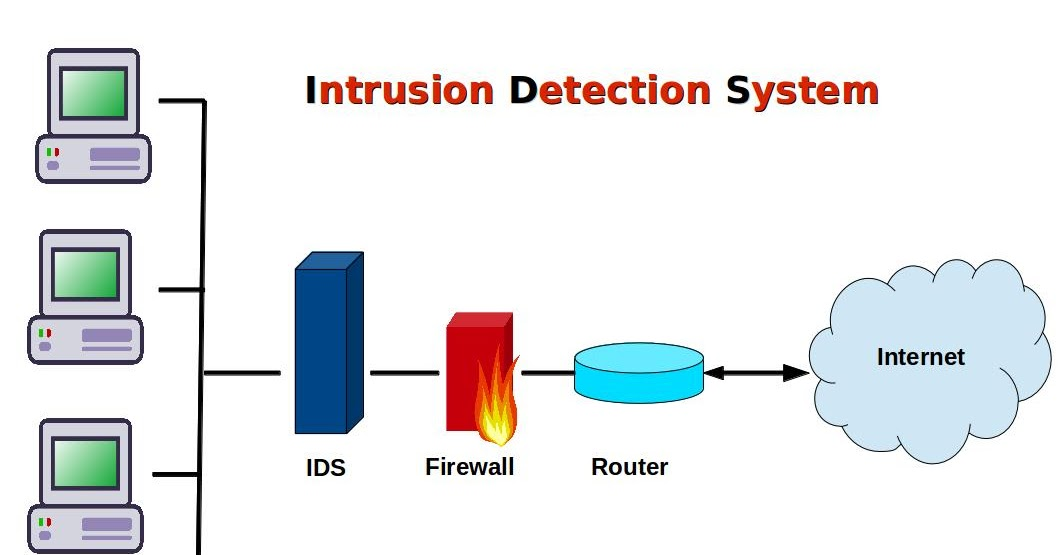</center>
In an ideal network security situation, both IDS and Firewalls work together to identify and log suspicious traffic or packages being transmitted. The IDS is able to provide real-time data on the network and notifies the Firewall of any anomalies. While the need for either of these technologies is largely dictated by the needs of the organization or individuals sharing a network, the Firewall is an important consideration for any size network, as it can be a very cost-effective measure of web security.
 hiveblocks
hiveblocks