Despite all the constitutional technologies in today's cameras, some key selections ought to be created before happening a photograph shoot...
How well-prepared is your camera before you begin to require pictures? Some necessary selections ought to be created to make sure you get the results you would like.
Factors just like the file format you utilize will play a key role, as will the drive mode setting, the metering mode, whether or not to shoot stills or movies (or both) and whether or not to require advantage of stabilisation (camera and/or lens) and integral aids like face and eye detection or dynamic vary changes
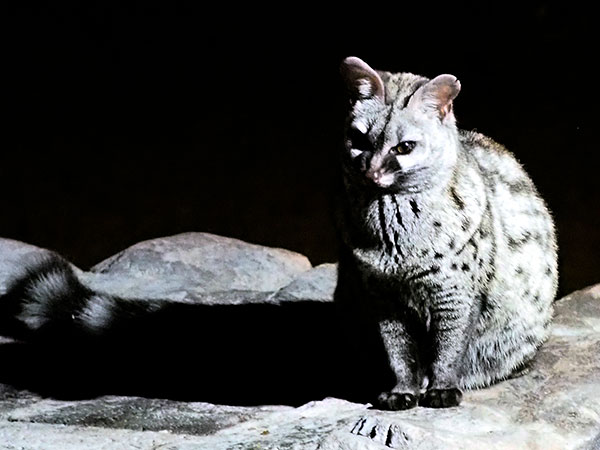

The effects of JPEG compression show up in difficult shooting things. This photograph of a small-spotted genet was taken in the dark within the Witsand space in Republic of South Africa with a M4/3 camera mistreatment AN ISO setting of twenty five,600 and AN exposure of 1/13 second at f/5.6 (the most aperture of the lens at the 140mm focal length).
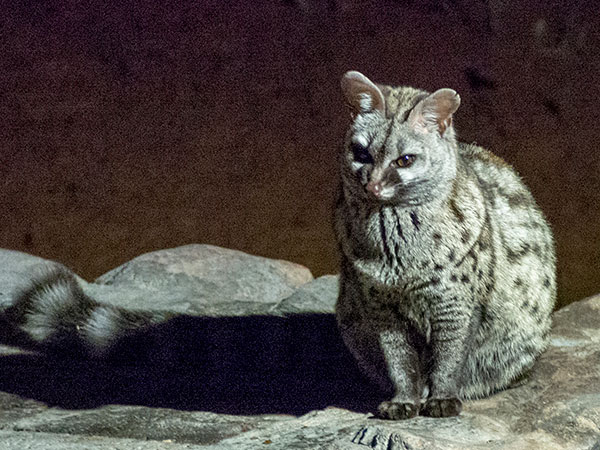

The raw file captured at the same time with the JPEG enabled a lot of detail to be extracted and delivered higher color copy and a wider dynamic point the image.
1. File Format
JPEG is taken into account the 'universal' file format as a result of it may be viewed on any screen, output to any printer or device and keep quickly and simply as a result of it mechanically compresses the information to cut back the number of cupboard space needed. Shooting JPEGs is best once you simply wish to post pictures on sharing websites, or read them on TV sets and monitor screens.
Because it may be displayed on any device, JPEG is that the format of selection for pictures that ar needed quickly, like those sent to publishers or submitted for competitions. it's supported by all image editors and industrial printing instrumentality. Most cameras offer many settings covering the image size (in pixels) and quality (level of compression) for JPEGs recorded within the camera. an equivalent is true once you save JPEGs via a picture editor.
Unfortunately, every time a JPEG image is saved, it'll be compressed, which implies the a lot of typically a JPEG file is saved, the a lot of knowledge is lost. once many re-savings, the standard of the image can have deteriorated perceptibly. thus most photographers notice it's helpful to own AN uncompressed file containing all the image knowledge recorded once the shot was captured in addition, if just for archiving.
Two choices ar available: bicker and therefore the camera's native raw format. the previous is editable, whereas raw files got to be reborn into editable formats. Raw files (often shown as 'RAW', though the term isn't AN acronym) record data captured by the camera. This info passes straight to the memory card while not the camera's micro chip adjusting it.
Most cameras save the information in a very proprietary format determined by the camera manufacturer, which needs compatible conversion code (some of questionable functionality). this may be inconvenient for photographers WHO wish ends up in a rush
While most enthusiasts' cameras support each JPEG and raw capture, few offer bicker as a native capture possibility, as a result of they're typically large and take a protracted time to method. Raw files may be reborn into 16-bit TIFFs to get the most quantity of image knowledge for redaction.
Files saved in bicker format may be uncompressed or losslessly compressed, each choices retentive all (or most) of the first knowledge. emended bicker files ar simply reborn into 8-bit JPEG format wherever they're going to retain the benefits of getting been emended within the higher bit depth format (as shown within the illustration below) however be straightforward to look at, share and print.
Professional photographers and high enthusiasts typically capture still pictures as raw files, that ar either uncompressed or compressed losslessly to retain all the image knowledge. this enables the creative person to regulate sharpness, contrast, brightness vary, color balance, saturation and different parameters while not compromising image quality.
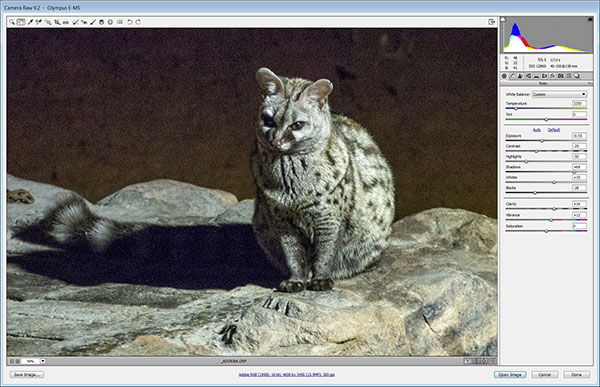
The space for a preferred conversion code, Adobe Camera Raw, shows the changes that may be created whereas process raw files. Raw files may also be saved in pettifoggery format with a 16-bit depth, that retains all the image information and provides further scope for tweaking the file.
When speed is a vital criterion, several photographers elect to shoot solely JPEGs. If you are operating to a point in time, shooting to output for on-line viewing or printing in an exceedingly newspaper, shooting JPEGs makes a lot of sense. a small loss of image information is essentially digressive all told these things and JPEGs may be sent via Wi-Fi directly from the camera to a wise device for transmission to a home office or posting in an exceedingly diary.
Where speed is digressive, raw files square measure desirable as they supply the utmost quantity of image information to figure with once written material shots. All raw-capable cameras allow you to capture raw and JPEG files at the same time via a RAW+JPEG setting and a few offer changes to the scale and quality of the JPEG shots, a handy feature wherever space for storing is proscribed.
Shooting raw files involves many caveats. Raw files square measure larger than JPEGs and, albeit the most recent cameras will record bursts of raw files nearly as quick as JPEGs, the buffer memory for storing them quickly cannot hold as several files. Entry-level cameras typically run out of house once fewer than ten raw files square measure recorded, and users should usually stay up for thirty seconds or a lot of till the memory is cleared and also the camera is ready to capture a lot of shots.
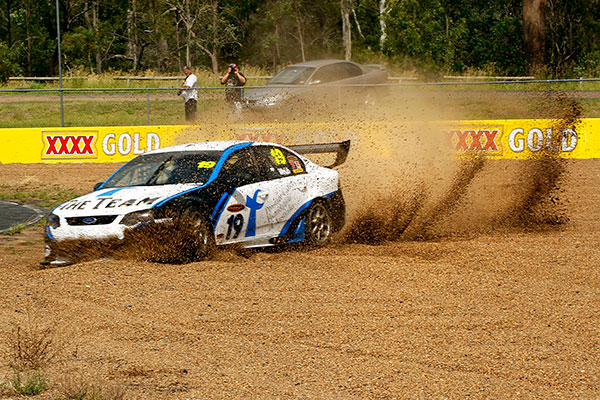

Professional sports photographers usually record pictures in JPEG format, notably after they recognize they're going to need to use the continual shooting mode and once the photographs ar destined for newspapers or websites.
2. Drive mode alternative
While it is simple to be seduced by claims of quick continuous shooting rates, continuous shooting has positive and negative aspects. Unless you would like to capture a sequence of shots covering a selected action, most cameras can deliver a better proportion of sharp shots with the single-frame mode, notably once subjects ar moving.

When the direction of movement is sure and you'll be able to shoot from a hard and fast position, frame rates slower than 5 frames/second will give smart coverage of action.
Avoid the burst mode if the action peaks during a instant, like at the highest of a jump or dive or the end of a race. Unless the camera supports speeds quicker than ten frames/second (fps), there is rarely enough time for the camera to 'find' the topic and you may solely get close to misses.
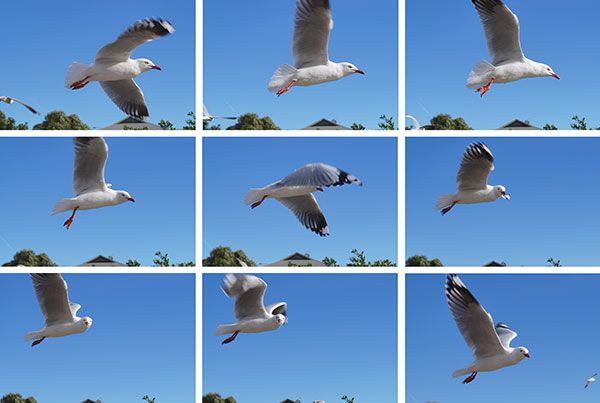

Even once cameras support continuous shooting quicker than ten frames/second, it will be tough to trace subjects like birds on the wing and you wish quick and correct trailing AF to get sharp pictures for the whole sequence.
Try to keep bursts short to confirm the photographs move quickly to the memory card, liberating the camera to shoot once more. In several cases, the action will be encompassed inside 3 to 5 frames, rental you pause a second then shoot another burst.
Check your camera's manual to seek out its limitations. several cameras lock the main target on the primary shot in a very burst. wherever continuous AF is supported, capture rates area unit usually slower, generally well thus. several burst modes cannot be employed in conjunction with flash and zoom and a few need shutter speeds of 1/30 second or quicker.
3. Metering
Selecting the optimum metering pattern for the topic permits the camera to guage the brightness level(s) and modify aperture and/or shutter speed settings properly, looking on the exposure mode you've got selected .
Most cameras give 3 metering options: multi-pattern critical (or matrix), centre-weighted average, and spot. Multi-pattern metering divides the topic space into multiple segments and one by one evaluates the sunshine level inside every, sometimes biasing the general exposure to counteract variations in brightness inside every section and between adjacent segments. Some cameras conjointly embody distance info from the optical device system and/or color information. Multi-pattern systems area unit smart all-rounders that employment with most varieties of scenes, as well as backlit subjects.
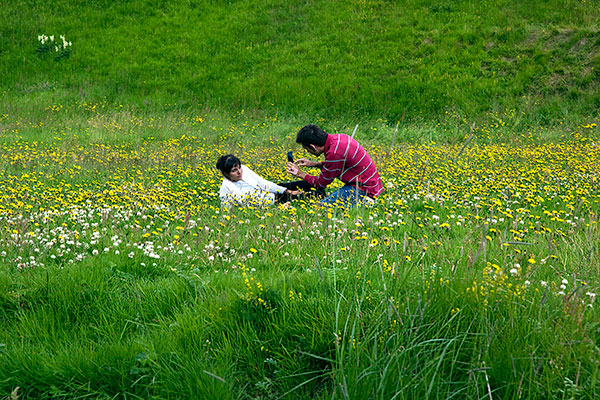

Centre-weighted average metering made a well-balanced exposure during this shot, that was crazy a 105mm lens on a 'full frame' DSLR camera.
Centre-weighted average metering integrates readings from everywhere the frame, inserting additional stress on the centre space. It’s effective for subjects with a median brightness vary wherever the most space of interest is central and might typically be a decent alternative for action shots.
Spot metering takes one reading from alittle space within the field of read. the scale of the spot is often expressed as a proportion of the sector of read, with typical spot sizes starting from one hundred and twenty fifth to regarding four wheel drive. alleged partial metering systems have slightly larger metering areas however work on constant principle.
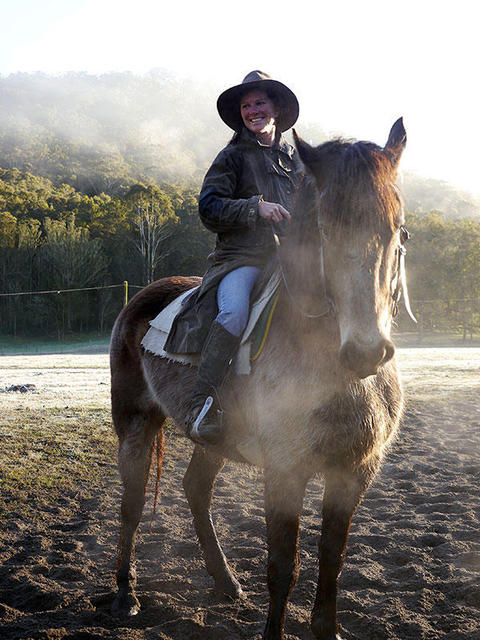

Spot metering on the rider's face delivered an accurate exposure for the most subjects during this scene, during which the wide brightness vary exceeds the sensor's recording capabilities. Note the blown-out highlights within the sky and therefore the near-black shadows.
Spot metering is right for backlit subjects and the other subject wherever there is a giant distinction in brightness between the topic and therefore the background. If the camera has focus following, it is also sensible for subjects that square measure in motion. merely centre the spot on the world you wish to live and press the AE lock button, then press the shutter unharness 0.5 means down. This locks the exposure (and focus), permitting you to re-compose and take the shot by pressing the shutter all the means down.
4. Stills or video?
With several new cameras recording 4K video clips, photographers have gained a replacement methodology for capturing momentary moments. the utmost frame resolution for 4K video is 4096 x 2160 pixels, though most cameras offer the 'consumer' 4K resolution of 3840 x 2160 pixels. Either way, a 4K video clip is similar to between eight.3 and 8.8 megapixels. every frame is printable at A3 size (420 millimetre on the long axis), that meets most amateur photographers' desires. Some cameras offer special 4K image modes for grabbing printable JPEG frames from show clips.

4K motion picture recording may be a good way to capture fugitive moments since you'll be able to recognize single 8-megapixel frames just like the one shown here from a recorded motion picture clip.
The main advantage of shooting motion in 4K video is comparatively high frame rates; generally twenty four frames/second. this can be abundant over most still cameras support and will offer enough sharp frames to hide many 'decisive moments'. However, 4K video needs the employment of quick, high-capacity memory cards, that ar high-ticket however scale back the chance of running out of memory.
5. Stabilisation
Although rarely necessary with wide angle lenses, once shooting with telephotograph lenses, stabilisation will create the distinction between a usable image and a dud. the chance of shots turning into blurred owing to camera shake will increase in proportion to the zoom magnification. you'll be able to forestall most camera shake by mounting the camera on a rack. However, this could not be convenient as a result of it limits the photographer's mobility.
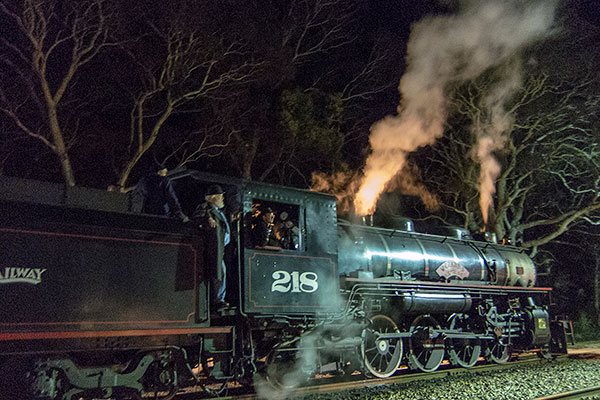
Without effective stabilisation, this hand-held shot of 1 of the zigzag zig Railway engines in the dark would are not possible because it needed a 1/8 second shutter speed with ISO 1600.
Stabilisation will be vital for hand-held shooting, significantly in low lightweight. It does not matter whether or not it's within the camera body or within the lens; each are helpful. In-camera sensor-shift systems work with any lens you attach to the camera, even optical lens lenses. the most recent cameras with this technology supply shake compensation in more than three.5 f-stops.
Many cameras with sensor-shift stabilisation supply many stabilisation modes to counteract vertical, horizontal and back/forth shaking. a number of these modes area unit offered on high-end stable lenses. stable lenses area unit sometimes larger, heavier and costlier than lenses while not integral stabilisation as a result of they contain a lot of parts.
6. Face detection/recognition technologies
Most imaging devices nowadays embrace face detection technology, sometimes as a part of their autofocusing systems. several cameras may also be programmed to recognise individual faces in pictures.
These technologies establish and target human faces and a few will 'recognise' pets. several allow you to program them to spot such people. skilled sports photographers use them for obtaining sharply-focused pictures for purchasers. Family photographers will realize them helpful for keeping centered on the 'star' during a scene.
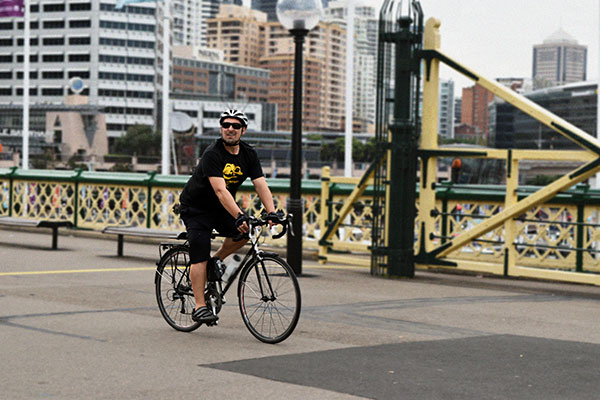

Face recognition technology makes it simple to get sharp pictures of individuals against probably distracting backgrounds.
Deciding that of those settings to use can depend upon the styles of footage you propose to require and the way they're going to be shared. If unsure, elect settings that offer you the most effective probabilities of recording the maximum amount image information as attainable and guaranteeing your footage are sharp.
The a lot of information you capture, the {better|the simpler} the image are to figure with and therefore the better your archived shots are if you would like to access them once more. it is simple to downmarket pictures for various applications; upscaling low-resolution shots is sometimes problematic. hiveblocks
hiveblocks