How our world has been made ???
https://steemitimages.com/DQmRmREsbHmtS1JZrxmTAXrbKpuDKDtxYTdpLz6g7VXuDYb/universe.png
"Scientific perspective"
Cosmology (from the Greek κόσμος, kosmos "world" and -λογία, -logia "study of") is the study of the origin, evolution, and eventual fate of the universe. Physical cosmology is the scientific study of the universe's origin, its large-scale structures and dynamics, and its ultimate fate, as well as the scientific laws that govern these areas.
The term cosmology was first used in English in 1656 in Thomas Blount's Glossographia, and in 1731 taken up in Latin by German philosopher Christian Wolff, in Cosmologia Generalis.
Religious or mythological cosmology is a body of beliefs based on mythological, religious, and esoteric literature and traditions of creation myths and eschatology.
Physical cosmology is studied by scientists, such as astronomers and physicists, as well as philosophers, such as metaphysicians, philosophers of physics, and philosophers of space and time. Because of this shared scope with philosophy, theories in physical cosmology may include both scientific and non-scientific propositions, and may depend upon assumptions that cannot be tested. Cosmology differs from astronomy in that the former is concerned with the Universe as a whole while the latter deals with individual celestial objects. Modern physical cosmology is dominated by the Big Bang theory, which attempts to bring together observational astronomy and particle physics; more specifically, a standard parameterization of the Big Bang with dark matter and dark energy, known as the Lambda-CDM model.
Theoretical astrophysicist David N. Spergel has described cosmology as a "historical science" because "when we look out in space, we look back in time" due to the finite nature of the speed of light.
Physics and astrophysics have played a central role in shaping the understanding of the universe through scientific observation and experiment. Physical cosmology was shaped through both mathematics and observation in an analysis of the whole universe. The universe is generally understood to have begun with the Big Bang, followed almost instantaneously by cosmic inflation; an expansion of space from which the universe is thought to have emerged 13.799 ± 0.021 billion years ago. Cosmogony studies the origin of the Universe, and cosmography maps the features of the Universe.
In Diderot's Encyclopédie, cosmology is broken down into uranology (the science of the heavens), aerology (the science of the air), geology (the science of the continents), and hydrology (the science of waters).
Metaphysical cosmology has also been described as the placing of man in the universe in relationship to all other entities. This is exemplified by Marcus Aurelius's observation that a man's place in that relationship: "He who does not know what the world is does not know where he is, and he who does not know for what purpose the world exists, does not know who he is, nor what the world is."
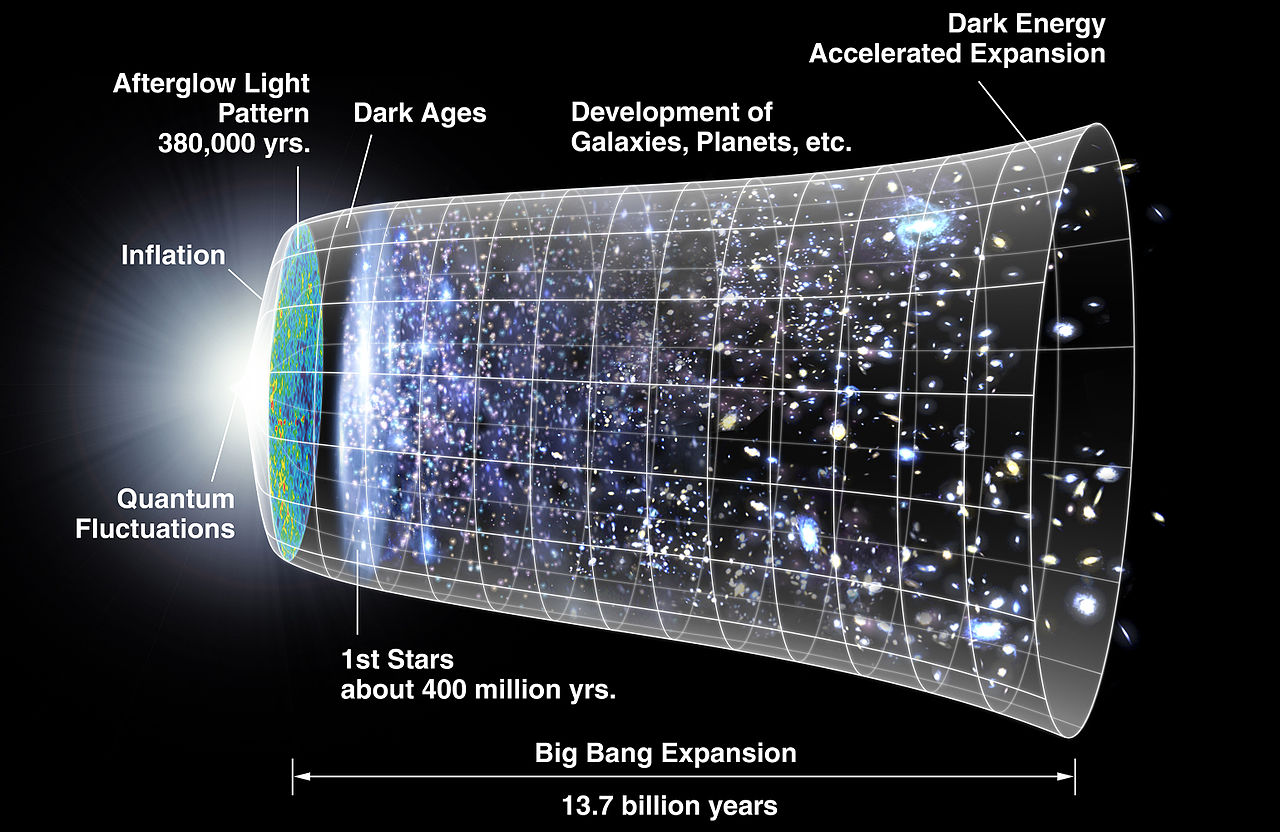
Physical cosmology
Main article: Physical cosmology
Physical cosmology is the branch of physics and astrophysics that deals with the study of the physical origins and evolution of the Universe. It also includes the study of the nature of the Universe on a large scale. In its earliest form, it was what is now known as "celestial mechanics", the study of the heavens. Greek philosophers Aristarchus of Samos, Aristotle, and Ptolemy proposed different cosmological theories. The geocentric Ptolemaic system was the prevailing theory until the 16th century when Nicolaus Copernicus, and subsequently Johannes Kepler and Galileo Galilei, proposed a heliocentric system. This is one of the most famous examples of epistemological rupture in physical cosmology.
When Isaac Newton published the Principia Mathematica in 1687, he finally figured out how the heavens moved. Newton provided a physical mechanism for Kepler's laws and his law of universal gravitation allowed the anomalies in previous systems, caused by gravitational interaction between the planets, to be resolved. A fundamental difference between Newton's cosmology and those preceding it was the Copernican principle—that the bodies on earth obey the same physical laws as all the celestial bodies. This was a crucial philosophical advance in physical cosmology.
Modern scientific cosmology is usually considered to have begun in 1917 with Albert Einstein's publication of his final modification of general relativity in the paper "Cosmological Considerations of the General Theory of Relativity" (although this paper was not widely available outside of Germany until the end of World War I). General relativity prompted cosmogonists such as Willem de Sitter, Karl Schwarzschild, and Arthur Eddington to explore its astronomical ramifications, which enhanced the ability of astronomers to study very distant objects. Physicists began changing the assumption that the Universe was static and unchanging. In 1922 Alexander Friedmann introduced the idea of an expanding universe that contained moving matter.
In parallel to this dynamic approach to cosmology, one long-standing debate about the structure of the cosmos was coming to a climax. Mount Wilson astronomer Harlow Shapley championed the model of a cosmos made up of the Milky Way star system only; while Heber D. Curtis argued for the idea that spiral nebulae were star systems in their own right as island universes. This difference of ideas came to a climax with the organization of the Great Debate on 26 April 1920 at the meeting of the U.S. National Academy of Sciences in Washington, D.C. The debate was resolved when Edwin Hubble detected Cepheid Variables in the Andromeda galaxy in 1923 and 1924. Their distance established spiral nebulae well beyond the edge of the Milky Way.
Subsequent modelling of the universe explored the possibility that the cosmological constant, introduced by Einstein in his 1917 paper, may result in an expanding universe, depending on its value. Thus the Big Bang model was proposed by the Belgian priest Georges Lemaître in 1927 which was subsequently corroborated by Edwin Hubble's discovery of the red shift in 1929 and later by the discovery of the cosmic microwave background radiation by Arno Penzias and Robert Woodrow Wilson in 1964. These findings were a first step to rule out some of many alternative cosmologies.
Since around 1990, several dramatic advances in observational cosmology have transformed cosmology from a largely speculative science into a predictive science with precise agreement between theory and observation. These advances include observations of the microwave background from the COBE, WMAP and Planck satellites, large new galaxy redshift surveys including 2dfGRS and SDSS, and observations of distant supernovae and gravitational lensing. These observations matched the predictions of the cosmic inflation theory, a modified Big Bang theory, and the specific version known as the Lambda-CDM model. This has led many to refer to modern times as the "golden age of cosmology".
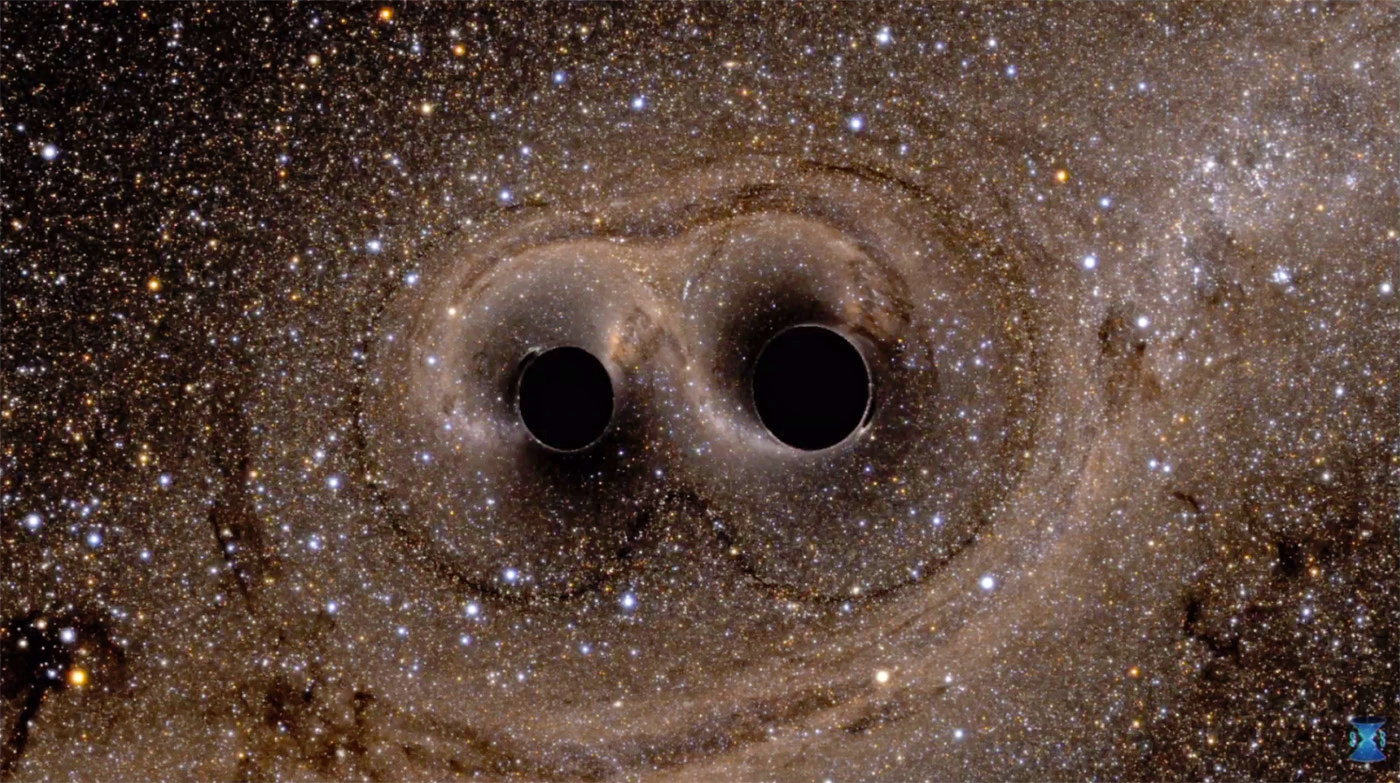

On 17 March 2014, astronomers at the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics announced the detection of gravitational waves, providing strong evidence for inflation and the Big Bang. However, on 19 June 2014, lowered confidence in confirming the cosmic inflation findings was reported.
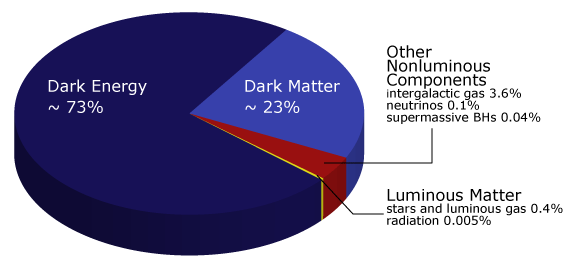
On 1 December 2014, at the Planck 2014 meeting in Ferrara, Italy, astronomers reported that the universe is 13.8 billion years old and is composed of 4.9% atomic matter, 26.6% dark matter and 68.5% dark energy.
thank's for reading.
continues ...
@timewarp
References :
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cosmology
https://steemitimages.com/DQmWpisRXDF56mV3DgzzPUxb3R2ozseR48YVr2YKtwtrBcV/upvote%20follow%20resteem.gif
 hiveblocks
hiveblocks