The discoveries of new living things and the changing ideas about the most effective ways of classifying life forms have resulted in the five kingdom classification system we use now. Today, the most generally accepted classification system contains five kingdoms: monerans, protists, fungi, plants, and animals.
As is often the case in science, not all scientists agree on this classification system. And this is an important idea for you to keep in mind. More research may someday show that different systems make more sense and better represent how living things evolved. But for now, this five kingdom system is a useful tool for studying living things - and that's exactly what taxonomy is all about.
<center></center>
<center>[Source](https://kidsbiology.com/biology-basics/)</center>
# Monerans
<p>
Bacteria are placed in the kingdom Monera. Monerans are unicellular organisms, or organisms that consist of only one cell. A moneran’s cell does not have its hereditary material enclosed in a nucleus, the structure that in other cells houses this important material. In addition to a nucleus, moneran cells lack many other structures found in other cell. Because of their unique characteristics, monerans are considered to be very distantly related to the other kingdoms.
<center>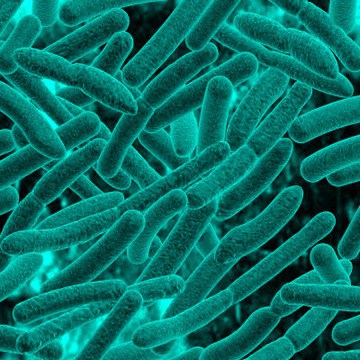</center>
<center>[Source](https://www.educandose.com/reino-moneras/)</center>
Like other organisms, monerans can be placed into two categories, based on how they obtain energy. Organisms that obtain energy by making their own food are called autotrophs. Such a name makes a lot of sense since the prefix auto - means self and the root word - troph means food. Organisms that cannot make their own food are called heterotrophs. The prefix hetero means other. Can you explain why heterotroph is a good name for such organisms? Heterotrophs may eat autotrophs in order to obtain food or they may eat other heterotrophs. But all heterotrophs ultimately rely on autotrophs for food.
Scientists have evidence that monerans were the earliest life forms on Earth. They first appeared about 3.5 billion years ago.
<center></center>
<center>[Source](http://www.kuensting.org/school/bb/special_topics/photosynthesis.htm)</center>
<center>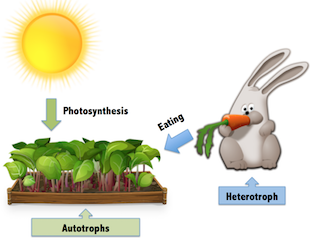</center>
<center>[Source](https://study.com/academy/lesson/autotrophs-vs-heterotrophs-lesson-for-kids-explanation-facts.html)</center>
# Protists
<p>
The kingdom Protista includes most of the unicellular (one-celled) organisms that have a nucleus. The nucleus controls the functions of the cell and also contains the cell's hereditary material .In addition; the cell of a protist has special structures that perform specific functions for the cell.
<center>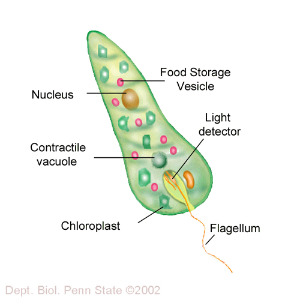</center>
<center>[Source](https://wikispaces.psu.edu/display/BIOL110F2013/Protists+I+-+Protists+with+Modified+Mitochondria%2C+Kingdoms+Euglenozoa+and+Alveolata)</center>
A number of protists are capable of animal like movement but also have some distinctly plantlike characteristics. Specifically, they are green in color and can use the energy of light to make their own food from simple substances. As you can imagine, such organisms are difficult, if not impossible, to classify using a two kingdom classification system. They are neither plants nor animals. Or perhaps they are both plants and animals. These puzzling organisms are one of reasons scientists finally decided to abandon the two kingdom system.
Protists were the first kind of cells that contain a nucleus. Ancient types of protists that lived millions and millions of year ago are probably the ancestors of fungi, plants, animals, and modern protists.
<center>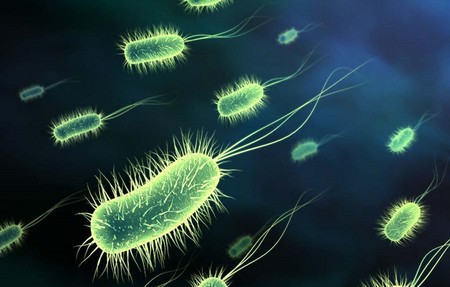</center>
<center>[Source](http://www.typesofeverything.com/types-of-bacteria/)</center>
# Fungi
<p>
as you might expect, the world's wide variety of fungi make up the kingdom fungi. Most fungi are multicellular organisms, or organisms that consist of many cells. Although you may not realize it, you may be quite familiar with fungi. Mushrooms are fungi. So are the molds that sometimes grow on leftover foods that have remained too long in the refrigerator. And the mildews that may appear as small black sports in damp basements and bathrooms are also fungi. For many years, fungi were classified as plants.
<center></center>
<center>[Source](https://www.setasdesiecha.com/hongos.html)</center>
However, they are quite different from plants in some basic ways. Their cells fit together in a different way. Their cell wall, a tough protective layer that surrounds the cell, is made of a different substance than the cell wall of plants. And most importantly, plants are able to use the energy of light to make their own food from simple substances. Fungi cannot. Like animals, fungi must obtain their food and energy from another source.
# <center>Are fungi autotrophs or heterotrophs?</center>
<p>
<center>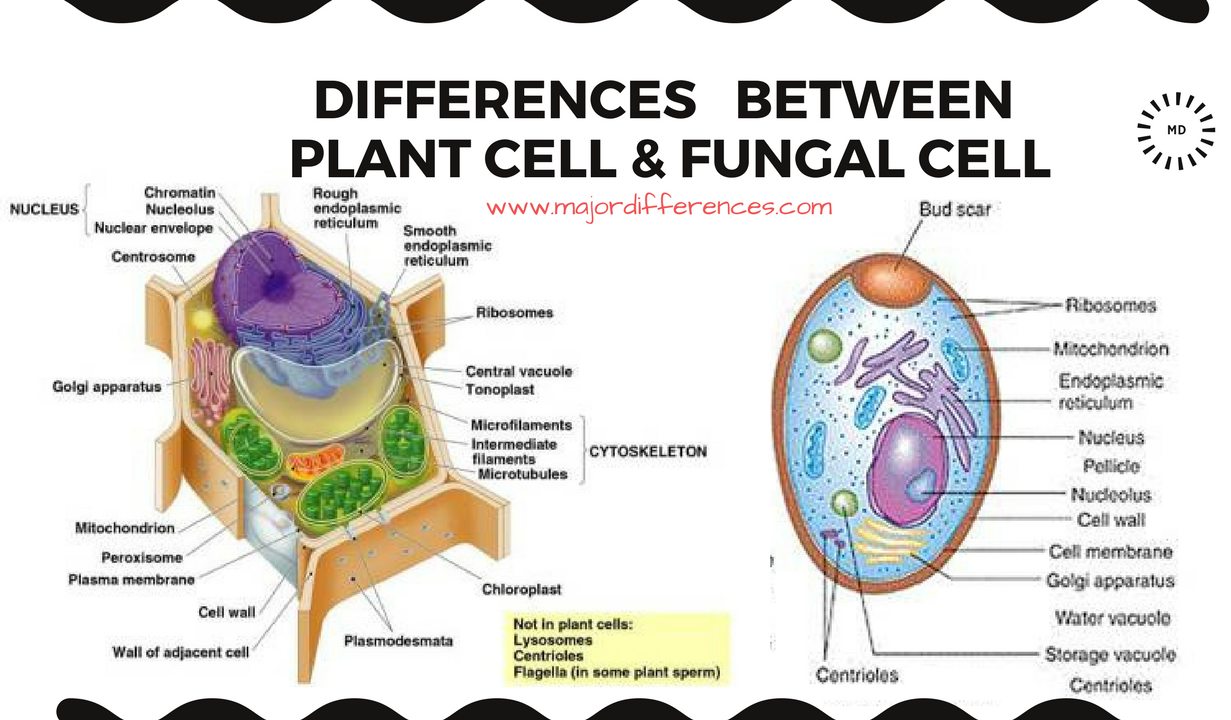</center>
<center>[Source](http://www.majordifferences.com/2017/09/6-differences-between-plant-cell-and.html#.WnIw-6jibIU)</center>
# Plants
<p>
Plants make up the kingdom Plantae. Most members of the plant kingdom are multicellular (many-celled ) autotrophs. You are probably quite familiar with members of this kingdom as it includes all the plants you have come to know by now, flowering plants, mosses, ferns, and certain algae, to name a few.
<center></center>
<center>[Source](https://okdiario.com/curiosidades/2016/10/07/como-respiran-plantas-435933)</center>
# Animals
<p>
Animals are multicellular organisms that comprise the kingdom Animalia. Like other multicellular organisms such as plants and certain fungi, animals have specialized tissues, and most have organs and organ systems. Unlike plants, animals are heterotrophs.
<center></center>
<center>[Source](http://www.1mobile.com/animals-for-kids-354748.html)</center>
Thanks to Taxonomy it is easy to classify organisms and establish parameters.
Source of information:
http://cienciasnaturales.carpetapedagogica.com/2012/08/los-cinco-reinos.html
http://www.areaciencias.com/los-5-reinos-de-los-seres-vivos.htm
https://kidsbiology.com/biology-basics/moneran/
https://www.definicionabc.com/ciencia/reino-monera.php
http://www.inbio.ac.cr/papers/hongos/intro.htm
 hiveblocks
hiveblocks