Viewing a response to: @mikewick77/intercellular-homeostasis
Nixtamalization Alkaline Blanching Nitrogen to Niacin Soaking corn kernels in an alkaline solution, like lime or wood ash, before cooking. This alkaline treatment releases niacin (vitamin B3) from the corn, making it bioavailable. Lime and ash are highly alkaline: the alkalinity helps the dissolution of hemicellulose, the major glue-like component of the maize cell walls, and loosens the hulls from the kernels and softens the maize. The tryptophan in corn proteins is made more available for human absorption, thus helping to prevent niacin deficiency. Tryptophan is the metabolic precursor of endogenous niacin (Vitamin B3). Nixtamalized corn has several benefits over unprocessed grain: It is more easily ground, its nutritional value is increased, flavor and aroma are improved, and mycotoxins are reduced by up to 97–100% (for aflatoxins). In the first step of nixtamalization, kernels of dried maize are cooked in an alkaline solution at or near the mixture's boiling point. Some of the corn oil is broken down into emulsifying agents (monoglycerides and diglycerides), while bonding of the maize proteins to each other is also facilitated. The divalent calcium in lime acts as a cross-linking agent for protein and polysaccharide acidic side chains. .. Nixtamalization: Definition: A traditional food processing technique for corn (maize) that involves cooking it in an alkaline solution. Impact on Nutrients: Nixtamalization can improve the bioavailability of some nutrients, including certain minerals and vitamin B3 Relevance to Homeostasis and Redox: The alkaline solution can enhance the solubility and bioavailability of certain metal ions, which can influence ion homeostasis and potentially impact redox-related enzyme activity. https://www.cimmyt.org/news/what-is-nixtamalization/ .. Nixtamalization convert Carbon, Nitrogen & Sulfur from Plant Biomass (weeds, tumbleweed, grass) into bioavailable Niacin & MSM pulp. all the green plants & even the dried up weeds, all of it is loaded with Nitrogen locked into complex compounds. needs a Alkaline Blanch, briefly immersed in boiling water. if the world goes upside down for a little while, this is both a simple food manufacturing process & medicine. out of yard weeds, a little fire & water & wood ash. .. Preparing the Alkaline Solution: Traditionally, a solution of water and lime (calcium hydroxide) was used. The lime (or wood ash) is typically dissolved in water and used to boil the corn. Cooking and Steeping: The corn kernels are boiled in the alkaline solution for a set amount of time, usually around an hour. The cooking time and soaking time are determined by the size of the corn kernels. After boiling, the corn is left to soak in the solution for several hours (8-12).
| author | mikewick77 |
|---|---|
| permlink | sukmv1 |
| category | intercellular |
| json_metadata | {"app":"hiveblog/0.1","links":["https://www.cimmyt.org/news/what-is-nixtamalization/"]} |
| created | 2025-04-11 20:42:36 |
| last_update | 2025-04-29 23:47:21 |
| depth | 1 |
| children | 6 |
| last_payout | 2025-04-18 20:42:36 |
| cashout_time | 1969-12-31 23:59:59 |
| total_payout_value | 0.000 HBD |
| curator_payout_value | 0.000 HBD |
| pending_payout_value | 0.000 HBD |
| promoted | 0.000 HBD |
| body_length | 2,789 |
| author_reputation | 545,063,717,246 |
| root_title | "Intercellular Homeostasis" |
| beneficiaries | [] |
| max_accepted_payout | 1,000,000.000 HBD |
| percent_hbd | 10,000 |
| post_id | 142,045,664 |
| net_rshares | 0 |
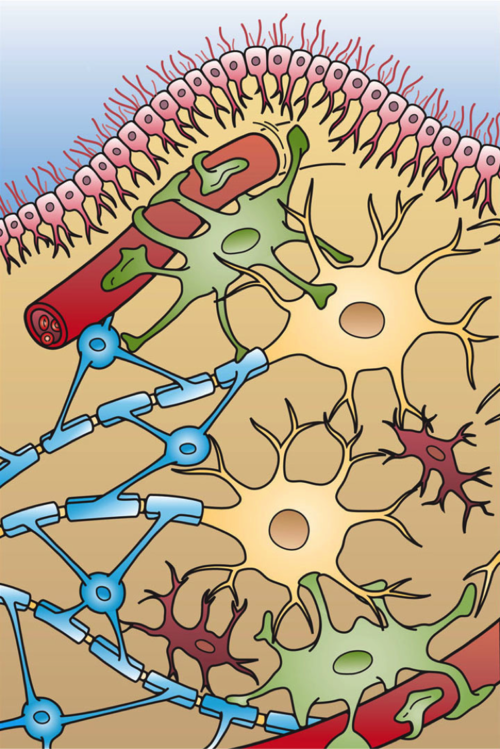 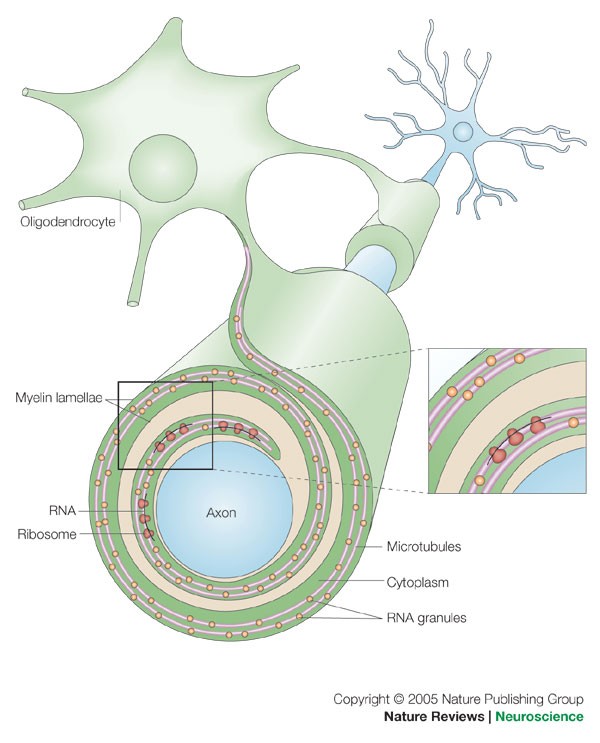 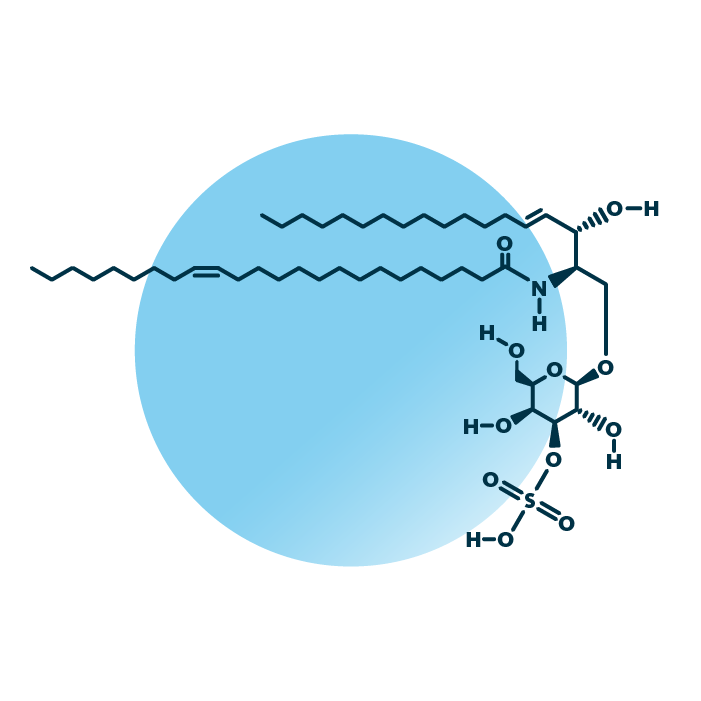 Sulfatide Ceramide Amyloid Precursor Protein (APP) Secretase Presenilin N-terminus Origin of Aβ: The Aβ peptide is cleaved from the amyloid precursor protein (APP) by enzymes called beta-secretase and gamma-secretase. Amyloid-beta (Aβ) Peptide: The core component of amyloid plaques is the Aβ peptide, a small protein (40-42 amino acids). Aggregation and Fibril Formation: Aβ peptides aggregate to form oligomers, then protofibrils, and finally, amyloid fibrils. These fibrils have a high β-sheet structure. β-Secretase (BACE1): BACE1 cleaves APP at the N-terminus of the Aβ peptide, initiating the amyloidogenic pathway. https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Amyloid-beta_precursor_protein https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Amyloid-beta_precursor_protein_secretase https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Presenilin .. Adipose Adipocyte Endoplasmic Reticulum Myalgic Encephalomyelitis Endothelin Myelin .. NMN: The NAD precursor at the intersection between axon degeneration and anti-ageing therapies NMN Nicotinic Acid Mononucleotide Wallerian Degeneration Toxic NMN Accumulation Axon Degeneration Programmed Axon Death SARM1 NMNAT2 Depletion Homocysteine Modulator Sirtuin AMPK p53 Hesperidin Glial Cells (Gliocytes) NMN: The NAD precursor at the intersection between axon degeneration and anti-ageing therapies https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0168010223000044 Nerve Fiber Degeneration https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/biochemistry-genetics-and-molecular-biology/nerve-fiber-degeneration Subcellular one carbon metabolism in cancer, aging and epigenetics https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/epigenetics-and-epigenomics/articles/10.3389/freae.2024.1451971/full .. Thionine Methyl CH3 Methionine MTHFS SAM-e Homocysteine SARM1 SARM1 activity is influenced by factors like homocysteine levels and S-adenosylmethionine (SAM). Increased homocysteine levels, often due to MTHFR mutations, can affect SARM1 activity and potentially lead to neurodegenerative processes.SAM, which is produced from methionine, is an important methyl donor that can influence SARM1 activity and nerve cell health. SARM1, homocysteine, and MTHFR are interconnected in a complex metabolic pathway that plays a role in various physiological processes, including nerve health and methylation reactions. MTHFR is an enzyme that regulates homocysteine levels, and mutations in the MTHFR gene can lead to elevated homocysteine, which in turn can affect SARM1 activity and downstream cellular processes. .. The most common side effects experienced by people who overdose on bromelain are nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, palpitation, indigestion, loss of appetite, headache, muscle pain, dizziness, drowsiness, and lethargy. What are the symptoms of b12 overload? (similar to overdose symptoms of: Magnesium, Bromelain, Nicotinamide Riboside) High doses of vitamin B-12, such as those used to treat a deficiency, might cause: Headache. Nausea and vomiting. Diarrhea. Fatigue or weakness. Tingling sensation in hands and feet.
| author | mikewick77 |
|---|---|
| permlink | suorx3 |
| category | intercellular |
| json_metadata | {"app":"hiveblog/0.1","image":["https://images.hive.blog/DQmX8UMjKHoEYqdNVRWzLW1dPWtRzbxwhfrnh68YQDV4hmz/500px-Glial_Cell_Types.png","https://images.hive.blog/DQmWna89jJTs996EL7jmaKwfqKpw59JUmgSAJwWu1oPQjaN/41583_2005_Article_BFnrn1743_Fig1_HTML.jpg","https://images.hive.blog/DQmUfpRZ47cSkYCmiXeCXDgYvJAxHG3LPhEYeJXPcEGVGy9/example_structure_of_sulfatide_42-2-2.png"],"links":["https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Amyloid-beta_precursor_protein"]} |
| created | 2025-04-14 02:22:15 |
| last_update | 2025-04-28 01:44:30 |
| depth | 2 |
| children | 0 |
| last_payout | 2025-04-21 02:22:15 |
| cashout_time | 1969-12-31 23:59:59 |
| total_payout_value | 0.000 HBD |
| curator_payout_value | 0.000 HBD |
| pending_payout_value | 0.000 HBD |
| promoted | 0.000 HBD |
| body_length | 3,522 |
| author_reputation | 545,063,717,246 |
| root_title | "Intercellular Homeostasis" |
| beneficiaries | [] |
| max_accepted_payout | 1,000,000.000 HBD |
| percent_hbd | 10,000 |
| post_id | 142,083,574 |
| net_rshares | 0 |
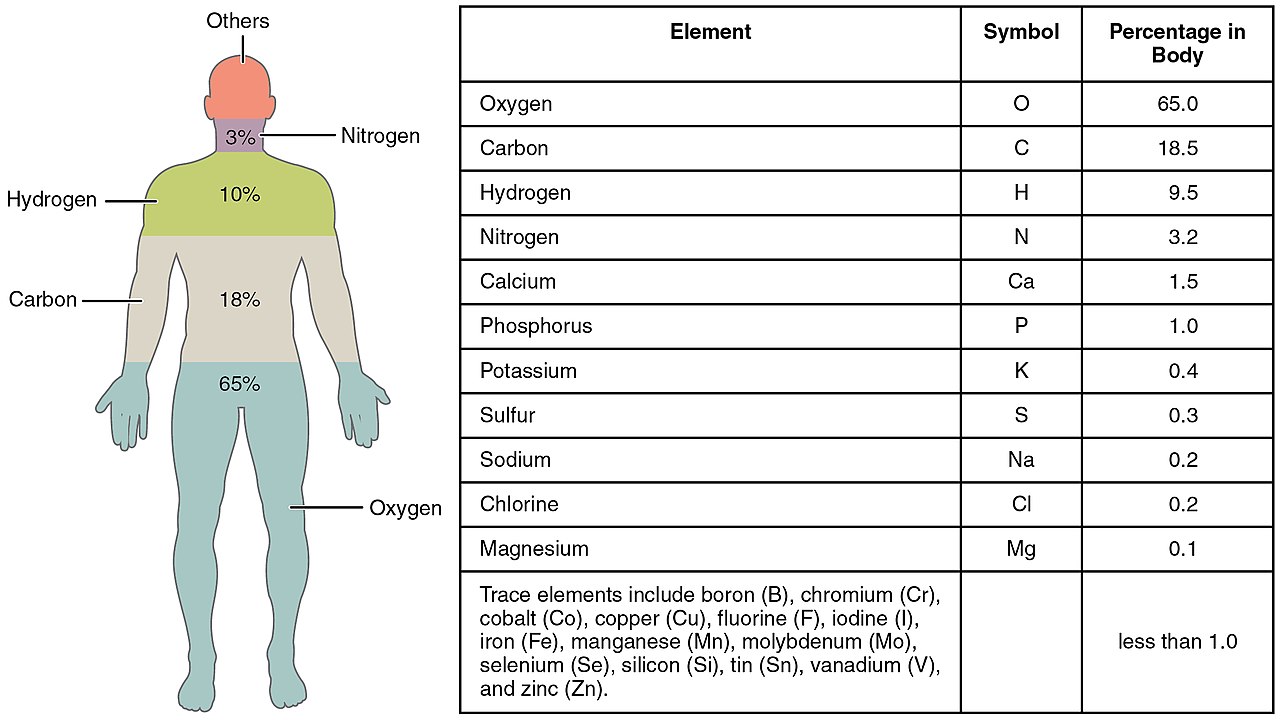 Biometals Metalloprotein Metalloenzyme Ion Homeostasis Glycosylation Metal Glycosylation Metalloglycobiology Congenital Disorders of Glycosylation (CDG) Biometal (biology) https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Biometal_(biology) Metalloglycobiology: The power of metals in regulating glycosylation https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0304416523001101 Hensen's Cell Schwann Cell Sulfatide Sulfoglycosphingolipid Lipidprotein Sphingomyelin Glycosphingolipid Sulfatides are glycolipids found in serum lipoproteins, they are also a major lipid component of myelin, the lipid coating around neuronal axons. Sulfatides, also known as sulfated galactocerebrosides, are a class of sulfolipids with a sulfate group attached to a carbohydrate. They are not only found in the nervous system but also in serum lipoproteins. https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hensen%27s_cell https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Schwann_cell https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sulfatide https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Glycocalyx .. Indole Alkaloid Conolidine https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Indole_alkaloid .. Cortisol Pregnane Glucocorticoid Galactosylceramide Ceramide Adrenal Tryptophan Indole Rings Microtubule Glycocalyx https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Eosinophilia%E2%80%93myalgia_syndrome .. On the emergence of P-Loop NTPase and Rossmann enzymes from a Beta-Alpha-Beta ancestral fragment https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7758060/ Microtubules play a crucial role in the formation and maintenance of myelin sheaths, particularly in oligodendrocytes, the cells responsible for myelin production in the central nervous system. These microtubules are essential for the extension of oligodendrocyte processes and the deposition of myelin. Specifically, Golgi outposts, specialized structures in oligodendrocytes, nucleate microtubules and are crucial for myelin sheath elongation. Microtubules are essential for maintaining the shape and structure of oligodendrocytes, which are responsible for wrapping axons in myelin. They act as "cellular highways" for transporting proteins and other materials necessary for myelin formation. Galactocerebroside (GalC), also known as galactosylceramide, is a type of cerebroside that is a major component of myelin in the nervous system. It's a glycolipid, meaning it's a lipid with a sugar molecule attached. GalC is synthesized from ceramide and UDP-galactose and is primarily found in neuronal cell membranes. The glycocalyx, a layer lining the luminal surface of endothelial cells in blood vessels, contains sulfatides as one of its components. Sulfatides are a type of glycolipid that contributes to the overall structure and function of the glycocalyx. Glycocalyx, sulfatide, ceramide, and myelin are all interconnected within the nervous system, with sulfatide and ceramide being key components of myelin and glycocalyx playing a role in the integrity of myelin. Sulfatide, a sulfated form of a galactosylceramide, is a major lipid component of myelin, which acts as an insulating sheath around nerve fibers. Ceramide is a lipid that serves as a building block for sulfatide and other myelin lipids. Glycocalyx, a layer of carbohydrates and proteins on cell surfaces, can interact with and influence myelin integrity. .. Niacin Microtubules Nicotinic acid, also known as niacin, can disrupt microtubules, which are part of the cytoskeleton, a network of protein filaments that helps maintain cell shape and supports intracellular transport. Specifically, high concentrations of nicotinic acid can lead to the disassembly of microtubules, potentially affecting processes that rely on this cytoskeletal structure. High concentrations of niacin can disassemble the microtubule cytoskeleton and degrade β-tubulin in cells. β-tubulin has a specific chemical structure, characterized by its ability to bind guanine nucleotides (GTP). Protofilaments associate laterally to form a hollow tube, with 13 protofilaments being the most common arrangement. β-tubulin, a subunit of microtubules, exhibits a complex chemical structure involving multiple secondary structural elements and crucial nitrogen-containing residues for its function. N-terminal domain: This region forms a Rossmann fold and binds the nucleotide (GTP/GDP). Some studies suggest that nicotinic acid's effects on microtubules may be related to changes in intracellular calcium levels. JPT2, or Jupiter Microtubule Associated Homolog 2, is an NAADP (nicotinic acid adenine dinucleotide phosphate) binding protein that is involved in NAADP-mediated Ca2+ release. NAADP is a signaling molecule that can trigger Ca2+ release from intracellular stores, and JPT2 is a protein that helps to facilitate this process.
| author | mikewick77 |
|---|---|
| permlink | sv6pd0 |
| category | intercellular |
| json_metadata | {"app":"hiveblog/0.1","image":["https://images.hive.blog/DQmcPuRTqG9rzp9x9j4r721SLrfU5LfAWPnVApQ7VXB8p1i/1280px-201_Elements_of_the_Human_Body-01.jpg"],"links":["https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Biometal_"]} |
| created | 2025-04-23 18:43:48 |
| last_update | 2025-04-29 00:54:39 |
| depth | 2 |
| children | 0 |
| last_payout | 2025-04-30 18:43:48 |
| cashout_time | 1969-12-31 23:59:59 |
| total_payout_value | 0.000 HBD |
| curator_payout_value | 0.000 HBD |
| pending_payout_value | 0.000 HBD |
| promoted | 0.000 HBD |
| body_length | 4,915 |
| author_reputation | 545,063,717,246 |
| root_title | "Intercellular Homeostasis" |
| beneficiaries | [] |
| max_accepted_payout | 1,000,000.000 HBD |
| percent_hbd | 10,000 |
| post_id | 142,277,988 |
| net_rshares | 0 |
T Cell Lymphocyte Cytotoxic T Cells Cytotoxic Proteins Perforin Granzymes Mannose https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Perforin-1 https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Granzyme_B .. Galactocerebroside (GalC) Glucocerebroside Glucocerebrosidase Glucocerebrosidase is an enzyme with glucosylceramidase activity that cleaves by hydrolysis the β-glycosidic linkage of the chemical glucocerebroside, an intermediate in glycolipid metabolism that is abundant in cell membranes (particularly skin cells). It is localized in the lysosome, where it remains associated with the lysosomal membrane. Domain I forms a three-stranded anti-parallel β-sheet. This domain contains two disulfide bridges that are necessary for correct folding. In Gaucher's disease, the enzyme glucocerebrosidase is nonfunctional and cannot break down glucocerebroside into glucose and ceramide in the lysosome. Affected macrophages, called Gaucher cells, have a distinct appearance similar to "wrinkled tissue paper" under light microscopy, because the substrates build-up within the lysosome. https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cerebroside .. Sulfatide Lysosulfatide Metachromatic Leukodystrophy (MLD) Arylsulfatase A (ARSA) .. Coenzyme Q CoQ10 Ubiquinone Quinone Benzoquinone Electron Donor refers to a molecule or substance that donates electrons to another molecule, effectively reducing its oxidation state. Antioxidants act as electron donors, donating electrons to free radicals (a type of ROS) to neutralize them. Examples of electron donors include Triarylamines, Nitrogen & Carbon Ring (Benzene, Phenol). In cellular respiration, glucose acts as an electron donor, donating electrons to electron carriers like NADH. These electrons are then used to generate energy in the form of ATP. Opposite Roles of Co-enzyme Q10 and Formaldehyde in Neurodegenerative Diseases https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10624093/ .. nate electrons to other substances, typically in redox reactions. In biological systems, glucose is an example of an electron donor, donating electrons to electron carriers like NADH and FADH2 during cellular respiration. Quinones (like ubiquinone or CoQ) are also electron donors, playing a key role in the electron transport chain. Quinones can be synthesized through various methods, including chemical oxidation of phenols, hydroquinones. key synthesis methods: 1. Chemical Oxidation: Phenols: Phenols can be oxidized to quinones using various oxidizing agents, including sodium dichromate and sulfuric acid. .. Oil Nitrogen Sulfur Oxygen Hydrogen Coenzyme A (CoA) Butyryl-CoA Glycine Glutamine Taurine Butyrate Sulfide Quinone Oxidoreductase (SQR) is an enzyme that plays a crucial role in sulfide homeostasis and metabolism in various organisms. It catalyzes the oxidation of sulfide (S2- or HS-) to zero-valent sulfur. Cofactor Binding: SQR utilizes a flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) cofactor, which is noncovalently bound to the enzyme during or after synthesis. Nitrogen is a fundamental element in amino acids, which are the building blocks of proteins, including SQR. Therefore, adequate nitrogen is necessary for the overall synthesis of SQR protein. SQR is a flavoprotein, meaning it requires FAD as a cofactor for its function. FAD is derived from riboflavin (vitamin B2). Riboflavin, through its conversion to FAD, acts as a critical cofactor for SQR, enabling the enzyme to perform its vital functions in sulfide metabolism. While riboflavin is required for the conversion of hydrogen sulfide to sulfite via SQOR, it also plays a role in managing sulfite levels through its involvement with other enzymes like glutathione reductase. Sulfide:quinone oxidoreductase (SQR) is a membrane-bound flavoprotein enzyme that plays a crucial role in sulfide metabolism. It catalyzes the oxidation of sulfide (H₂S) to elemental sulfur, a process involved in sulfide detoxification, energy generation by contributing electrons to electron transport chains, and sulfide homeostasis. Sulfate is the final oxidation product of sulfur metabolism. Riboflavin involvement in the conversion of sulfite to sulfate, riboflavin's role in optimizing the earlier steps of the sulfur cycle indirectly affects the overall balance of sulfur compounds. Flavoproteins have either FMN (flavin mononucleotide) or FAD (flavin adenine dinucleotide), both having Nitrogen. .. A Catalytic Trisulfide in Human Sulfide Quinone Oxidoreductase Catalyzes Coenzyme A Persulfide Synthesis and Inhibits Butyrate Oxidation https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2451945619303150
| author | mikewick77 |
|---|---|
| permlink | svenbr |
| category | intercellular |
| json_metadata | {"app":"hiveblog/0.1","links":["https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Perforin-1"]} |
| created | 2025-04-28 01:40:36 |
| last_update | 2025-06-17 13:34:30 |
| depth | 2 |
| children | 0 |
| last_payout | 2025-05-05 01:40:36 |
| cashout_time | 1969-12-31 23:59:59 |
| total_payout_value | 0.000 HBD |
| curator_payout_value | 0.000 HBD |
| pending_payout_value | 0.000 HBD |
| promoted | 0.000 HBD |
| body_length | 4,601 |
| author_reputation | 545,063,717,246 |
| root_title | "Intercellular Homeostasis" |
| beneficiaries | [] |
| max_accepted_payout | 1,000,000.000 HBD |
| percent_hbd | 10,000 |
| post_id | 142,362,369 |
| net_rshares | 0 |
MCT Medium Chain Triglyceride Fractionated Oil Fractionation Deacidification Lipase Esterification C8 C10 The synthesis of MCTs involves the combination of MCFAs and glycerol, often with the help of catalysts, to create the desired triglyceride structure. This process can be achieved through esterification or acidolysis reactions. Fatty Acid Methyl Esters: MCTs are often produced from fatty acid methyl esters, which are extracted from sources like coconut or palm kernel oil. Catalysis: This reaction can be catalyzed by enzymes (like lipases) or chemical catalysts, such as acid catalysts or metal catalysts. Acidolysis: Alternatively, MCTs can be synthesized through acidolysis, where MCFAs are exchanged with fatty acids present in long-chain triglycerides. This process is often facilitated by a chemical catalyst like sulfuric acid. Temperature and Pressure: Esterification reactions can be conducted at various temperatures and pressures, ranging from 170°C/40 kPa to 140-160°C. .. Caprylic acid, also known as octanoic acid, is synthesized through the oxidation of its corresponding aldehyde, octanal. This process transforms the aldehyde group (CHO) into a carboxylic acid group (COOH). Oxidation: In the case of caprylic acid, the C8 aldehyde is octanal, which has the structural formula CH3(CH2)6CHO. Process: The oxidation reaction involves the addition of an oxygen atom to the aldehyde group, converting it into a carboxylic acid group. Result: This oxidation produces caprylic acid, CH3(CH2)6COOH. Oxidants: Various oxidizing agents can be used, including hydrogen peroxide, potassium permanganate, and other reagents. reducing agent (also known as a reductant, reducer, or electron donor) is a chemical species that "donates" an electron to an electron recipient (called the oxidizing agent. Examples of substances that are common reducing agents include hydrogen, carbon monoxide, the alkali metals, formic acid, oxalic acid, and sulfite compounds. Citric acid is known for its ability to reduce metal ions, like gold and silver, which is crucial for the formation of nanoparticles. citric acid and its salts are valuable tools in nanoparticle synthesis, acting as both reducing agents and stabilizers, influencing the size, shape, and stability of the resulting nanoparticles. .. Fractionated coconut oil and MCT (medium-chain triglyceride) oil are essentially the same thing; they are both derived from coconut oil and contain a high concentration of MCTs. The key difference is that MCT oil is a specific, concentrated version of MCTs, while fractionated coconut oil is a broader term that can refer to oils with varying MCT compositions. .. Le Chatelier's Principle: This principle helps understand how changes in temperature, like heating, can shift the equilibrium of reactions involving pH. Common Ion Effect: Adding a salt containing a common ion to a solution of a weak acid or base will suppress the dissociation of the weak acid or base, shifting the equilibrium and affecting the pH. This is a direct application of Le Châtelier's principle, where the addition of the common ion is the disturbance. How pH Changes Shift Equilibrium: Adding Acid Decreasing pH: Increases H+ concentration The equilibrium will shift to the left (towards reactants) to consume the excess H+ ions. Adding Base Increasing pH: Decreases H+ concentration (increases OH- concentration). The equilibrium will shift to the right (towards products) to produce more H+ ions and partially offset the reduction in H+. MCTs and DHT Potential DHT Blocking: Some research, primarily in test-tube and animal studies, suggests that MCTs, particularly lauric acid, may inhibit the enzyme 5-alpha reductase, which converts testosterone to DHT. DHT Synthesis: DHT was initially synthesized by hydrogenating testosterone. .. Why no pH for vegetable oil? Vegetable oil is primarily composed of lipids (fats) and does not contain water in a way that would allow for a meaningful pH measurement. Measuring Acidity in Oil: Instead of pH, the acidity of vegetable oil can be measured by its acid value (AV), which reflects the amount of free fatty acids present. This is often determined by a process called titration, where a solution of known acidity is added to the oil until the oil's acidity is neutralized. Importance of Acidity: The acidity of vegetable oil is an indicator of its quality, as it can increase with time and storage conditions due to the breakdown of triglycerides into free fatty acids. For example, virgin olive oils have a relatively low acidity, typically below 2%. .. Glycerol/Glycerin: This three-carbon alcohol molecule is the backbone structure of all triglycerides. Glycerin and glycerol are the same molecule (1,2,3-propanetriol), and they form the backbone of triglycerides. Triglycerides: These are lipids (fats) composed of glycerol bonded to three fatty acid chains. Medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs) are a specific type of triglyceride where the fatty acid chains are medium in length (6 to 12 carbon atoms).
| author | mikewick77 |
|---|---|
| permlink | svsw1i |
| category | intercellular |
| json_metadata | {"app":"hiveblog/0.1"} |
| created | 2025-05-05 18:15:18 |
| last_update | 2025-05-13 07:02:09 |
| depth | 2 |
| children | 0 |
| last_payout | 2025-05-12 18:15:18 |
| cashout_time | 1969-12-31 23:59:59 |
| total_payout_value | 0.000 HBD |
| curator_payout_value | 0.000 HBD |
| pending_payout_value | 0.000 HBD |
| promoted | 0.000 HBD |
| body_length | 5,105 |
| author_reputation | 545,063,717,246 |
| root_title | "Intercellular Homeostasis" |
| beneficiaries | [] |
| max_accepted_payout | 1,000,000.000 HBD |
| percent_hbd | 10,000 |
| post_id | 142,534,562 |
| net_rshares | 0 |
 OSF3 Niosomes Ketogenesis Ketone Bodies Acetate Citrate Mitochondria Acetoacetate ketones produced from omega-3 fatty acids may reduce cognitive deterioration in old age. Ketoacidosis is known to occur in untreated type I diabetes (see diabetic ketoacidosis) and in alcoholics after prolonged binge-drinking without intake of sufficient carbohydrates (see alcoholic ketoacidosis). .. Emulsify Emulsification Surfactant Fats Oil Water Salts Broth Emulsification in cooking refers to mixing oil and water-based liquids like broth, where the oil is dispersed into tiny droplets within the water, forming a stable mixture. Broth: In broth-based dishes, the fat released during cooking can emulsify with the water, creating a creamy or opaque texture. Salt's Role: While salt doesn't directly emulsify, it can influence the stability of an emulsion by affecting the interactions between the oil and water phases. .. Honey Olive Oil Lemon Squeeze 3-4 lemons and place the juice in a glass jar. Add the honey and the olive oil, and with a wooden spoon mix the ingredients until a smooth blend is obtained. Keep the remedy in the fridge with a lid on the jar. Pour the oil into a small saucepan and gently heat. Add the honey and slowly stir until the honey and oil are combined. Leave to cool, after which it will thicken. Give it a good whisk to transform it into a thick satiny syrup. Caramelization of glucose, a chemical process involving sugar breakdown under heat, can impact polyphenol synthesis. This interaction is complex, with studies showing both enhancement and reduction of polyphenol-related reactions. .. Olive Oil Olive Leaf Oleuropein Oleocanthal monounsaturated fatty acids MUFA triglyceride glycerol polyphenol phenol phenylethanoid phenethyl alcohol benzene secoiridoid glycoside hydroxytyrosol elenolic acid glucose glycolipid glucoside .. Phenolic Compounds in Honey and Their Relationship with Antioxidant Activity, Botanical Origin, and Color https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8614671/ .. Peroxiredoxin, a family of enzymes, relies on a key cysteine residue within its active site for its catalytic activity. This cysteine, often referred to as the "peroxidatic cysteine," is crucial for reducing peroxides like hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). The active site cysteine undergoes oxidation by H2O2, forming a sulfenic acid, which is then recycled back to the thiol form, distinguishing the three enzyme classes. Neutralization of Trace Metals: During the refining of edible oils, citric acid can be added to neutralize trace metals that can catalyze oxidation reactions. How Citric Acid and Citrus Essential Oils Combat Lipid Oxidation: Citric Acid: Citric acid, found in many citrus fruits, is a natural antioxidant that can scavenge free radicals and inhibit lipid oxidation. It can also enhance the nutritional value of the oil. Antioxidants: Antioxidants are reducing agents that play a crucial role in preventing oxidation reactions, especially by neutralizing free radicals. In a redox reaction, antioxidants donate electrons to unstable free radicals, stabilizing them and preventing damage to other molecules. This process makes the antioxidant itself the reducing agent, as it is oxidized by donating electrons. .. Trihydroxy Benzoic Acid Alpha-Glucoside Diglucosyl Gallic Acid Syringic Acid Quercitannic Acid Tannin https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Syringic_acid .. Caramelized Glucose Glucose caramelization products (GCPs), can undergo polyphenol synthesis under specific conditions. Caramelization can lead to the formation of compounds that exhibit antioxidant activity, often similar to that of polyphenols. Caramelization products, especially those formed in the presence of amino compounds, can exhibit antioxidant activity, polyphenols and reductones as key components in these products. While true polyphenols are not necessarily formed directly during caramelization, the resulting compounds often have similar properties to polyphenols, such as radical scavenging activity and antioxidant capacity against lipid oxidation. Reductones are reducing agents (antioxidants). Some are fairly strong acids. Examples of reductones are glucic acid, reductic acid and ascorbic acid. Glucic acid is an acid produced by the action of acids on cane-sugar or of alkalis on glucose. https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Reductone https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Glycolic_acid https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Glucic_acid https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Phloroglucinol https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Salicylic_acid https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ceramide .. N-Acetyl Cysteine and Catechin-Derived Polyphenols: A Path Toward Multi-Target Compounds Against Alzheimer's Disease https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.3233/JAD-200067?url_ver=Z39.88-2003&rfr_id=ori:rid:crossref.org&rfr_dat=cr_pub%20%200pubmed Results: We found that EPIC-PYR, CAT-PYR, and CAT-PhG inhibit human tau aggregation and significantly increase neuritogenesis in a dose-dependent manner. Interestingly, modification with a phloroglucinol group yielded the most potent molecule of those evaluated, suggesting that the phloroglucinol group may enhance neuroprotective activity of the catechin-derived compounds. Also, as observed with cathechins, NAC promotes neuritogenesis and inhibits tau self-aggregation, possibly through a different pathway. .. Potent Thrombolytic Effect of N-Acetylcysteine on Arterial Thrombi https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/10.1161/circulationaha.117.027290 Impact on Von Willebrand Factor (VWF): Research suggests NAC can affect VWF, a protein involved in platelet aggregation and blood clot formation. By reducing VWF's ability to bind platelets, NAC may help prevent clots. A Heterocycle is a cyclic compound (ring structure) where some of the atoms in the ring are not carbon. Combining NAC with polyphenols to form heterocycles can potentially enhance their individual benefits by creating new molecules with unique properties. Some studies suggest that glycolic acid can enhance the antioxidant activity of certain polyphenols, potentially improving their effectiveness when combined in skincare formulations. Vitamin E and melatonin have been shown to have a synergistic effect with glycolic acid, potentially improving their antioxidant activity and protection against liposome peroxidation. Salicylic acid is a colorless (or white), bitter-tasting solid, it is a precursor to and a metabolite of acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin). .. has to be broken up almost at the atomic level, the Reducing Agents do one thing, but its also the Benzene Rings of the Polyphenol that seem to act as atomistic fish hooks & Reducing Agents the bait to the radical misfolding. and somehow the Sulfur gets the fish hooks into the deep waters. .. Strong acids induce amyloid fibril formation of β2-microglobulin via an anion-binding mechanism https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8564678/ anions in promoting fibril formation of amyloid protein .. Oxidative Strong Acids Anion Hydrochloric Acid Sulfuric Acid vs Antioxidant Cations Cation-π Polyphenol Cation-π interactions are noncovalent attractive forces between a positively charged entity (cation) and the π-electron cloud of an aromatic ring. In the context of cation-π interactions and chloride, the interaction between a cation (e.g., Na+, K+) and a chloride ion (Cl-) is driven by the attraction of the positive charge of the cation to the negative charge of the chloride ion. Cation-π interactions are a type of non-covalent interaction between a cation and a π system (a system of shared electrons, often found in aromatic molecules). Antioxidants often interact with metal ions (cations) in their mechanisms, for example, some antioxidants can bind to metal ions and prevent them from participating in free radical reactions. Cations are positively charged ions, such as Na+, K+, and Mg2+. Na+, K+, and Mg2+ salts are compounds containing sodium, potassium, and magnesium ions, respectively, paired with a counterion (like chloride, sulfate, etc.) to form a neutral compound. Cation-π interactions are a type of non-covalent interaction where a positively charged cation (like an alkali metal ion or an organic cation) interacts with the π-electron cloud of an aromatic ring. π-electron cloud: Aromatic rings, like benzene, have delocalized electrons that form a cloud above and below the ring, which can interact with other molecules. In biological systems: Cation-π interactions play a role in protein folding, channel blocking, and biomolecular condensates. Chloride ion (Cl-): A negatively charged ion, it's one of the main anions in body fluids and plays a role in maintaining electrolytic balance and nerve function. .. Cation Metals + Chloride Acids - Sodium Chloride (NaCl, common table salt). Potassium Chloride (KCl). Magnesium Chloride (MgCl2) .. Weak & Strong Acids vs Soft & Hard Acids .. Cation–π Interaction Origin of the effect https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cation%E2%80%93%CF%80_interaction Benzene, the model π system, has no permanent dipole moment, as the contributions of the weakly polar carbon–hydrogen bonds cancel due to molecular symmetry. However, the electron-rich π system above and below the benzene ring hosts a partial negative charge. A counterbalancing positive charge is associated with the plane of the benzene atoms, resulting in an electric quadrupole (a pair of dipoles, aligned like a parallelogram so there is no net molecular dipole moment). The negatively charged region of the quadrupole can then interact favorably with positively charged species; a particularly strong effect is observed with cations of high charge density. .. Progressive fuzzy cation-π assembly of biological catecholamines https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/sciadv.aat7457 Tannic acid- and N-acetylcysteine-chitosan-modified magnetic nanoparticles reduce hepatic oxidative stress in https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0927776524000493
| author | mikewick77 |
|---|---|
| permlink | svygm8 |
| category | intercellular |
| json_metadata | {"app":"hiveblog/0.1","image":["https://images.hive.blog/DQmYFbKCs3VAKJGJuM3WrzPceEmRupcZLKXvUh9UhFubrn6/Schematic_2.jpg"],"links":["https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8614671/"]} |
| created | 2025-05-08 18:27:45 |
| last_update | 2025-05-24 19:44:21 |
| depth | 2 |
| children | 0 |
| last_payout | 2025-05-15 18:27:45 |
| cashout_time | 1969-12-31 23:59:59 |
| total_payout_value | 0.000 HBD |
| curator_payout_value | 0.000 HBD |
| pending_payout_value | 0.000 HBD |
| promoted | 0.000 HBD |
| body_length | 10,188 |
| author_reputation | 545,063,717,246 |
| root_title | "Intercellular Homeostasis" |
| beneficiaries | [] |
| max_accepted_payout | 1,000,000.000 HBD |
| percent_hbd | 10,000 |
| post_id | 142,608,963 |
| net_rshares | 0 |
Brain Metabolism Folate / Cobalamin Methylfolate Methylcobalamin Acetylcysteine Cysteine Methyl Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Alcohol Ethanol Acetaldehyde 8-OHdG MTHFR Urea Folate Methylfolate (5-MTHF) Tannic Acid N-Acetylcysteine Chitosan The body needs adequate amounts of folate, vitamin B6, and vitamin B12 to produce cysteine. Folate derived from the Latin word “folium,” which means leaf. Leafy vegetables are among the best dietary sources of folate. The active form of vitamin B9 is a type of folate known as 5-methyltetrahydrofolate (5-MTHF) Before entering your bloodstream, your digestive system converts folate to the biologically active form of vitamin B9 5-MTHF. Folate: This is the natural form of vitamin B9 found in foods like leafy greens and citrus fruits. Methylfolate: This is the active, biologically available form of folate that the body uses. It's also known as 5-methyltetrahydrofolate (5-MTHF) or L-methylfolate. Folic Acid: This is a synthetic form of folate, often found in supplements and fortified foods. .. Folate vs Folic Acid Methylcobalamin vs Cyanocobalamin https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/methylcobalamin-vs-cyanocobalamin .. Inductive Effect: The carbon-hydrogen bonds in a methyl group are slightly polarized, with the electrons being pulled towards the more electronegative carbon atom. This creates a partial negative charge on the carbon, which then pushes electron density towards the atom or group it's attached to. Hyperconjugation: In some cases, especially when there's an adjacent pi system (like in an aromatic ring), hyperconjugation can also contribute to the electron-donating effect. Hyperconjugation involves the interaction of the sigma bonds in the methyl group with the pi system, leading to a more stable and electron-rich environment. Electron-Donating Character: This electron-donating behavior can be observed in various reactions, including electrophilic aromatic substitution where methyl groups often direct incoming electrophiles to the para and ortho positions (the most stable positions due to the increased electron density). In the brain, glucose metabolism and cation transport are tightly linked and essential for neuronal function. Glucose, the brain's primary fuel, is transported across the blood-brain barrier and into cells via specific glucose transporters (GLUTs). Cation transport, particularly of sodium and potassium, is vital for maintaining membrane potential and action potentials in neurons. Glucose metabolism relies on a complex interplay of facilitated diffusion and active transport mechanisms, including the role of cations. Diseases like Alzheimer's and Huntington's are associated with abnormalities in glucose metabolism and cation transport, affecting neuronal function and leading to cognitive and behavioral deficits. .. Ethanol metabolism: The good, the bad, and the ugly https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0306987720300797 .. Folate Precursors Biosynthesis The main precursors for folate biosynthesis are GTP, p-aminobenzoic acid (PABA), and glutamate. GTP (Guanosine Triphosphate): This nucleoside triphosphate provides the building blocks for the pterin portion of the folate molecule. PABA (Para-aminobenzoic acid): This molecule is crucial for the formation of the pteroyl component of folate. Glutamate: This amino acid is incorporated into the folate structure and is essential for its biological activity. .. Toxic Trans Fat Elaidic Acid Saturated CETP Cholesteryl Ester Transfer Protein Vitamins like B12, and supplements, like carnitine, can play a role in lipid metabolism and energy production, potentially impacting how the body processes fats, including trans fats. Vitamin B12 is a cofactor for mitochondrial enzymes involved in fatty acid metabolism. Carinatine plays a role in transporting long-chain fatty acids into mitochondria for energy production. .. Monoterpenes (Phenol) Polyphenol Volatility: Monoterpenes are generally volatile, while polyphenols are not. Examples: Monoterpenes: Limonene (citrus fruits), menthol, eucalyptol. Polyphenols: Flavonoids (found in fruits and vegetables), anthocyanins (responsible for red and purple colors in plants). Ascorbic acid (C6H8O6) has a different molecular structure compared to citric acid (C6H8O7). Astaxanthin A Xanthophyll Carotenoid found in marine organisms, with studies showing it can be 6,000 times more potent than vitamin C and 550 times more potent than vitamin E. High ORAC Value: Astaxanthin has a very high Oxygen Radical Absorbance Capacity (ORAC) value, indicating its strong antioxidant ability to fight free radicals. Carotenoids: Carotenoids are a group of naturally occurring pigments found in plants and animals, responsible for various colors, including yellow, orange, and red. Xanthophylls: Xanthophylls are a specific subgroup of carotenoids that contain oxygen in their chemical structure. They are often associated with yellow and orange pigments. Astaxanthin's Unique Characteristics: Astaxanthin is a keto-carotenoid with both hydroxyl and ketone functional groups. .. Nitrogen Balance https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nitrogen_balance https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Oxygen_radical_absorbance_capacity https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_antioxidants_in_food .. Footprints of a Singular 22-Nucleotide RNA Ring at the Origin of Life https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7285048/ Scientists uncover a multibillion-year epic written into the chemistry of life https://phys.org/news/2024-05-scientists-uncover-multibillion-year-epic.html .. Acetylcysteinamide C5H10N2O2S C5H9NO3S Acetylcysteine Taurine Sulfoxide Sulfonyl Methane Dimethyl Methyl Methylene (Blue) Carotenoid (Red)
| author | mikewick77 |
|---|---|
| permlink | swva7n |
| category | intercellular |
| json_metadata | {"app":"hiveblog/0.1","links":["https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/methylcobalamin-vs-cyanocobalamin"]} |
| created | 2025-05-26 11:50:09 |
| last_update | 2025-06-08 21:06:42 |
| depth | 2 |
| children | 0 |
| last_payout | 2025-06-02 11:50:09 |
| cashout_time | 1969-12-31 23:59:59 |
| total_payout_value | 0.000 HBD |
| curator_payout_value | 0.000 HBD |
| pending_payout_value | 0.000 HBD |
| promoted | 0.000 HBD |
| body_length | 5,818 |
| author_reputation | 545,063,717,246 |
| root_title | "Intercellular Homeostasis" |
| beneficiaries | [] |
| max_accepted_payout | 1,000,000.000 HBD |
| percent_hbd | 10,000 |
| post_id | 142,972,450 |
| net_rshares | 0 |
 hiveblocks
hiveblocks