Viewing a response to: @mikewick77/sukmv1
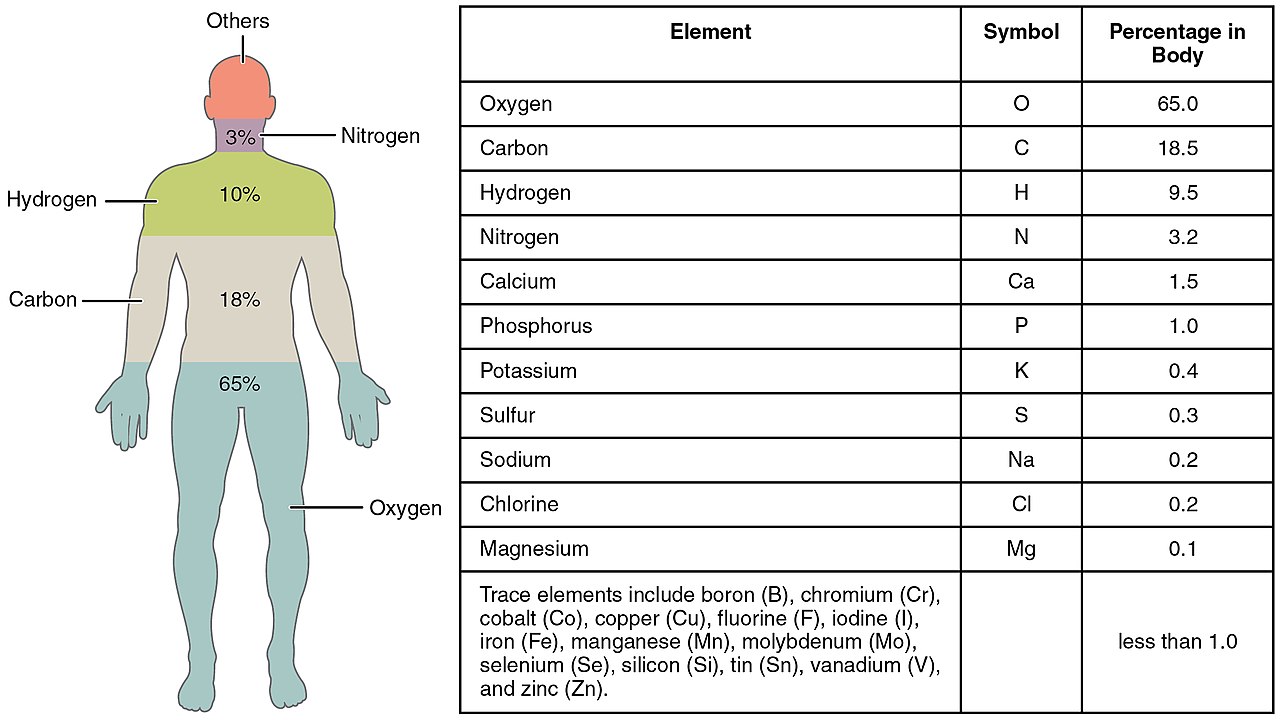 Biometals Metalloprotein Metalloenzyme Ion Homeostasis Glycosylation Metal Glycosylation Metalloglycobiology Congenital Disorders of Glycosylation (CDG) Biometal (biology) https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Biometal_(biology) Metalloglycobiology: The power of metals in regulating glycosylation https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0304416523001101 Hensen's Cell Schwann Cell Sulfatide Sulfoglycosphingolipid Lipidprotein Sphingomyelin Glycosphingolipid Sulfatides are glycolipids found in serum lipoproteins, they are also a major lipid component of myelin, the lipid coating around neuronal axons. Sulfatides, also known as sulfated galactocerebrosides, are a class of sulfolipids with a sulfate group attached to a carbohydrate. They are not only found in the nervous system but also in serum lipoproteins. https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hensen%27s_cell https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Schwann_cell https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sulfatide https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Glycocalyx .. Indole Alkaloid Conolidine https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Indole_alkaloid .. Cortisol Pregnane Glucocorticoid Galactosylceramide Ceramide Adrenal Tryptophan Indole Rings Microtubule Glycocalyx https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Eosinophilia%E2%80%93myalgia_syndrome .. On the emergence of P-Loop NTPase and Rossmann enzymes from a Beta-Alpha-Beta ancestral fragment https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7758060/ Microtubules play a crucial role in the formation and maintenance of myelin sheaths, particularly in oligodendrocytes, the cells responsible for myelin production in the central nervous system. These microtubules are essential for the extension of oligodendrocyte processes and the deposition of myelin. Specifically, Golgi outposts, specialized structures in oligodendrocytes, nucleate microtubules and are crucial for myelin sheath elongation. Microtubules are essential for maintaining the shape and structure of oligodendrocytes, which are responsible for wrapping axons in myelin. They act as "cellular highways" for transporting proteins and other materials necessary for myelin formation. Galactocerebroside (GalC), also known as galactosylceramide, is a type of cerebroside that is a major component of myelin in the nervous system. It's a glycolipid, meaning it's a lipid with a sugar molecule attached. GalC is synthesized from ceramide and UDP-galactose and is primarily found in neuronal cell membranes. The glycocalyx, a layer lining the luminal surface of endothelial cells in blood vessels, contains sulfatides as one of its components. Sulfatides are a type of glycolipid that contributes to the overall structure and function of the glycocalyx. Glycocalyx, sulfatide, ceramide, and myelin are all interconnected within the nervous system, with sulfatide and ceramide being key components of myelin and glycocalyx playing a role in the integrity of myelin. Sulfatide, a sulfated form of a galactosylceramide, is a major lipid component of myelin, which acts as an insulating sheath around nerve fibers. Ceramide is a lipid that serves as a building block for sulfatide and other myelin lipids. Glycocalyx, a layer of carbohydrates and proteins on cell surfaces, can interact with and influence myelin integrity. .. Niacin Microtubules Nicotinic acid, also known as niacin, can disrupt microtubules, which are part of the cytoskeleton, a network of protein filaments that helps maintain cell shape and supports intracellular transport. Specifically, high concentrations of nicotinic acid can lead to the disassembly of microtubules, potentially affecting processes that rely on this cytoskeletal structure. High concentrations of niacin can disassemble the microtubule cytoskeleton and degrade β-tubulin in cells. β-tubulin has a specific chemical structure, characterized by its ability to bind guanine nucleotides (GTP). Protofilaments associate laterally to form a hollow tube, with 13 protofilaments being the most common arrangement. β-tubulin, a subunit of microtubules, exhibits a complex chemical structure involving multiple secondary structural elements and crucial nitrogen-containing residues for its function. N-terminal domain: This region forms a Rossmann fold and binds the nucleotide (GTP/GDP). Some studies suggest that nicotinic acid's effects on microtubules may be related to changes in intracellular calcium levels. JPT2, or Jupiter Microtubule Associated Homolog 2, is an NAADP (nicotinic acid adenine dinucleotide phosphate) binding protein that is involved in NAADP-mediated Ca2+ release. NAADP is a signaling molecule that can trigger Ca2+ release from intracellular stores, and JPT2 is a protein that helps to facilitate this process.
| author | mikewick77 |
|---|---|
| permlink | sv6pd0 |
| category | intercellular |
| json_metadata | {"app":"hiveblog/0.1","image":["https://images.hive.blog/DQmcPuRTqG9rzp9x9j4r721SLrfU5LfAWPnVApQ7VXB8p1i/1280px-201_Elements_of_the_Human_Body-01.jpg"],"links":["https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Biometal_"]} |
| created | 2025-04-23 18:43:48 |
| last_update | 2025-04-29 00:54:39 |
| depth | 2 |
| children | 0 |
| last_payout | 2025-04-30 18:43:48 |
| cashout_time | 1969-12-31 23:59:59 |
| total_payout_value | 0.000 HBD |
| curator_payout_value | 0.000 HBD |
| pending_payout_value | 0.000 HBD |
| promoted | 0.000 HBD |
| body_length | 4,915 |
| author_reputation | 545,063,717,246 |
| root_title | "Intercellular Homeostasis" |
| beneficiaries | [] |
| max_accepted_payout | 1,000,000.000 HBD |
| percent_hbd | 10,000 |
| post_id | 142,277,988 |
| net_rshares | 0 |
 hiveblocks
hiveblocks